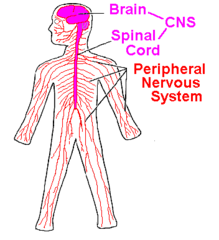
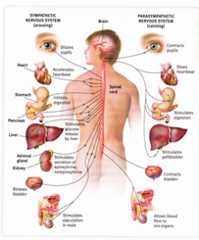
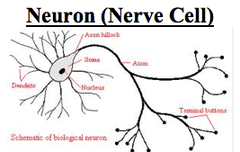
CNS
central nervous system contains brain and the spinal cord
PNS
peripheral nervous system consisting of nerves and ganglia that lie outside of the brain and spinal cord
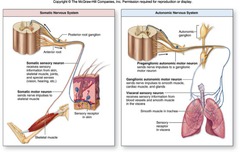
somatic nervous system
the division of the PNS that provides the motor innervation of skeletal muscles; voluntary nervous(skeletal muscle) system
dermatomes
innervated skin segmented by cutaneous sensory branches of a single spinal nerve {areas of body or cell junctions composed of thickened plasma membranes joined by filaments (skin segments) supply the body and other organs with nerves}
autonomic (visceral)
involuntary nerve neurons reflexes or activation of glands and or smooth and cardiac muscles in the PNS
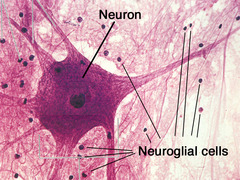
neuron (nerve cell)
cell of the nervous system specialized to generate and transmit electrical signals actin potentials and graded potentials)
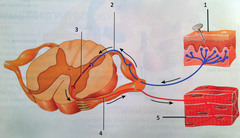
sensory/afferent
nerves that contain processes of sensory neurons and carry impulses to the CNS
motor/efferent
nerves that carry impulses leaving the brain and spinal cord , destined for effectors (signals away from the CNS to PNS)
ganglion/nucleus
enlargement in a nerve; collection nerve cell bodies outside the CNS
convergent neuron
multiple or many neurons impulses activating a single axon (sensory)
divergent neurons
one axon synapses or activates on many neurons (motor)
ganglion
located in the PNS
nucleus
located in the spinal cord
sensory
located in receptor ending; respond to stimuli
nerve/tract
nerve: bundle of axons in the PNS; tract is a collection of axons in the CNS with the same origin, termination, and function.
plexus
junction of neurons that innervate a single or particular area, organ or place in the body, involves cranial nerve X
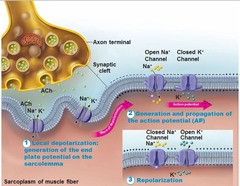
action potential
nerve or neuron impulses; what makes things happen in the body ( long membrane of muscle cells or nerve fibers)
neuroglia
non-excitable cells of neural tissue that support, protect, and insulate the neurons; glial cells
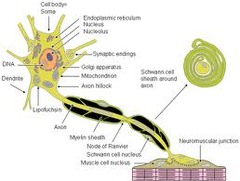
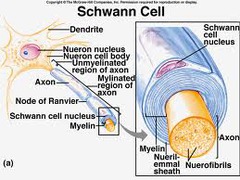
myelin
white matter; surround axons of nerves, cell membrane that causes impulses to travel faster; fatty insulating sheath surround all the smallest nerve fibers from fluids
oligodendeocytes
CNS supporting cell that composes myelin sheaths (cell wraps a few/multiple axons)
Schwann cells
PNS supporting cell; forms myelin sheaths and is vital peripheral nerve fiber regeneration
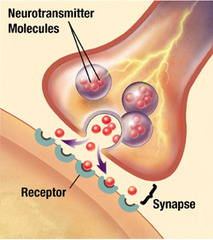
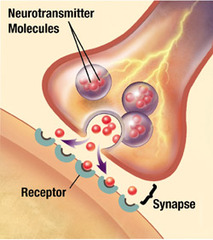
neurotransmitters
the chemical messengers released by neurons; may upon binding to receptors of neurons or effector cells, stimulate or inhibit those neurons or effector cells.
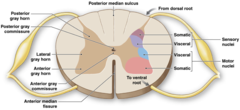
white matter
myelinated tissue only on axon located in the white substance of the CNS; impulses travel much faster, myelinated nerve fibers
gray matter
unmyelinated tissue; gray area in the CNS; contains neuronal cell bodies and their dendrites; travel much slower
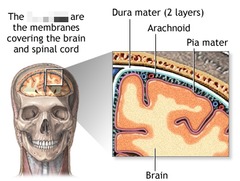
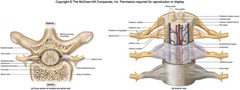
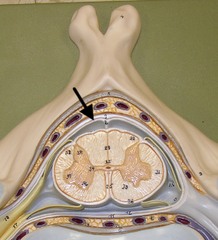
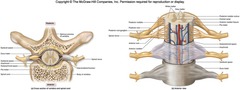
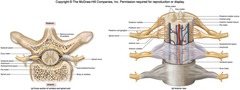
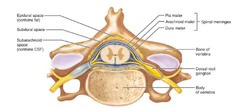
meninges of CNS
protective coverings of CNS
dura mater
toughest thick, outermost covering of the brain and spinal cord
arachnoid
weblike; middle layer fairly thick, holds most of the fluid
pia mater
delicate, very thin covering over the neurological (spinal) tissue (vascularily feeds spinal tissue; richly invested with tiny blood vessels; brain like cell phone wrap)
epidural space
the dura space between the meninges and bone filled with fatty tissue in the spinal cord
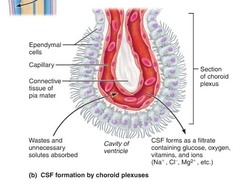
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
plasmalike fluid that fills the CNS cavities, surround CNS externally; fluid protects the brain and spinal cord
ventricles
cavities inside the brain; paired, inferiorly located chambers that function as major blood pumps (spaces inside the brain, or extend to the brain)
ependymal cells
compartments in the brain that produce CSF; and secrete fluid through membranes
arachnoid villi
knoblike projections; absorb cerebrospinal fluid into the venous blood of the sinus( part of circulation area)
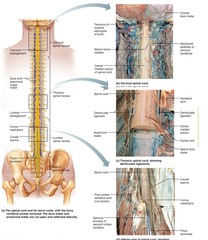
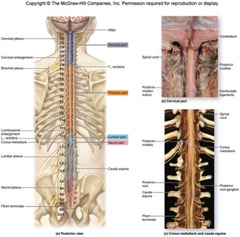
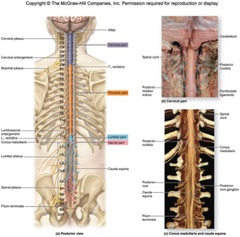
spinal cord
bundle of nerves that run from the brain to the first and third lumbar vertabrae and provides conduction pathway to and from the brain
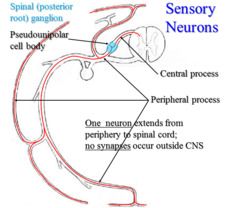
dorsal root
large nerve which enters the posterior end of the spinal cord (sensory)
dorsal root ganglion
mass of cell bodies in the sensory root neuron
ventral root
large nerve which exits/leaves the anterior the ventral surfase of the spinal cord motor root (sensation)
conus medullaris
central cone in the center of the spinal column and end unit of the spinal cord
cauda equina
mass of nerves that depart at the conus medullaris (sacrom); looks like a hairy horse tail/many hairs.
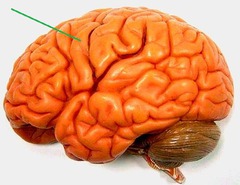
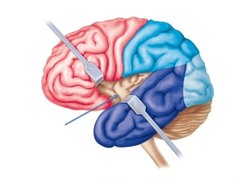
gyrus
outward fold of the surface of the cerebral cortex
sulcus
a furrow on the brain; shallow grooves (less deep than fissure)
fissure
deepest depression or inward folds in the brain; a groove or cleft (seperate large region of the brain)
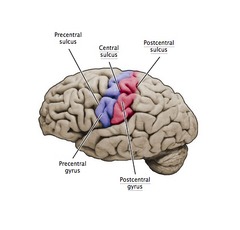
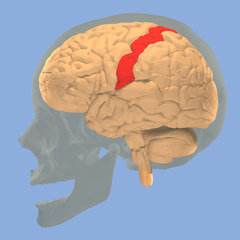
central sulcus
landmark, a cleft seperating the frontal lobe from the parietal lobes of the brain
pre-central gyrus
primary somatosenory cortex; function touch, body awareness (associated with motor signals/ muscle origin); bordering the central sulcus anteriorly
post-central gyrus
somato sensory cortex, outside layer of brain; primary motor cortex voluntary movement control-sensory of touch; posteriorly
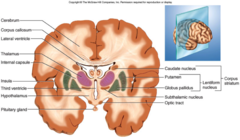
basal nuclei
involved in regulation of voluntary or rhythmic movement; gray mater at the base of the cerebral hemisphere
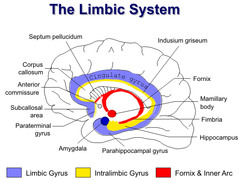
limbic system
intergration of sensory reception and memory; personality or life experiences (functional brain system involved in the emotional responses and memory formation)
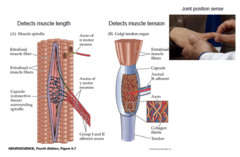
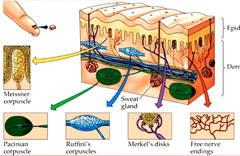
proprioceptors
awareness of limbs or parts of the body (located in the tendons or base of joint, and muscle)
function: locomotion, posture, and muscle tone
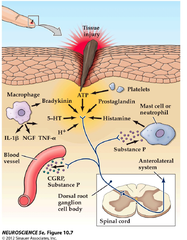
nociceptors
pain receptors; sensitive to potentially damaging stimuli that result in pain
mechanreceptors
must be touched or moved for muscle to contraction to activate (physical or mechanical)
auditory cilia
sensory system for sense of hearing , has hairs and includes both the sensory organs (ears) and auditory parts of the sensory system
vestibular cilia
located in the balance organ; use mechanical or operation cause/function require body movements to stimulate hairs; inner ear, larynx, nose
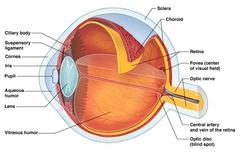
macula
senses work in straight line sensations or up and down/longitudial (central vision; light sensative layer of tissue lining the interior of the back of the eye; small spot, where vision is the keenest in the retina)
crista
rotational movements
touch receptors
mechnical receptor stimulated
chemoreceptors
sense chemicals dissolve in body fluid; receptor sensitive to various chemicals in solutions
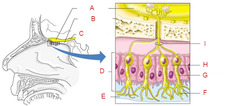
olfactory hairs
modified cilia projecting from olfactory cells in the mucosa of the nasal olfactory area. (not hairs but are dendrites/receivers)
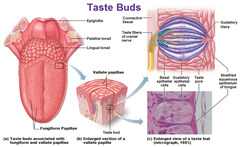
gustatory hairs
a long, spindlelike protrusion of epithelial cells that responds to dissolved chemicals (salvia) or several primary tastes, sweets, salty, tastes, bitter, etc.
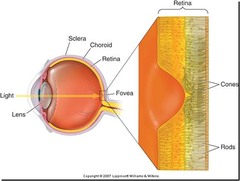
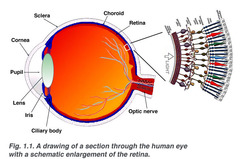
photoreceptors
specialized receptor cells that respond to light energy; and are sensitive to light located in the eye; rods and cones
rods
part of eye sees dim light, black and white and shades of gray in the retina
cones
part of eye responsible for color vision; requires bright light
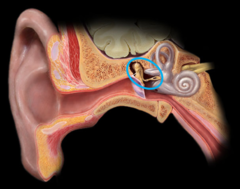
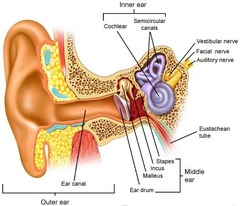
auditory ossicles
three bones in the middle ear
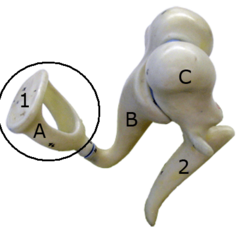
malleus
a small bone in the middle ear that transmits vibrations of the eardrum to the incus. (looks like hammer)
incus
a small anvil-shaped bone in the middle ear, transmitting vibrations between the malleus and stapes.
stapes
a small stirrup-shaped bone in the middle ear,transmitting vibrations from the incus to the inner ear. (touches the oval window)
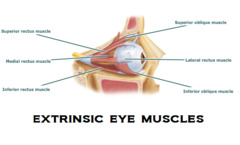
extrinsic eye muscles
outside, voluntary skeletal muscle that control movement of eyeball (II, IV, VI)( The extrinsic muscles are controlled by the somatic nervous system(voluntary)
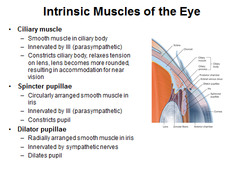
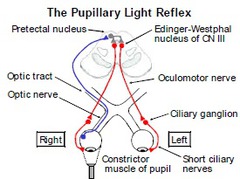
intrinsic eye muscles
The intrinsic muscles control the lens and pupil. The intrinsic eye muscles, (including the iris sphincter, radial pupilodilator muscles and the ciliary muscle), are under the control of the autonomic nervous system(involuntary)
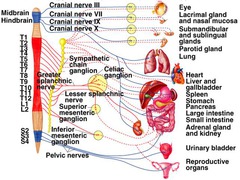
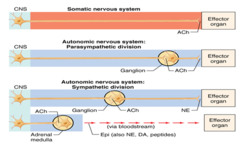
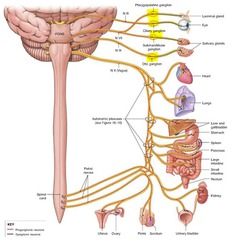
autonomic system
A part of the nervous system that regulates key involuntary functions of the body, including the activity of the heart muscle; the smooth muscles, including the muscles of the intestinal tract; and the glands.
sympathetic autonomic system
causes things to increase (up regulation) or increase body activity (accelerates the heart rate, constricts blood vessels, and raises blood pressure)
parasympathetic autonomic system
rest/digest (system which slows the heart rate, increases intestinal and gland activity, and relaxes sphincter muscles.) decrease regulation
preganglionic neuron (myelinated)
autonomic motor neuron that has its own cell body in the CNS and projects its axon on a peripheral ganglion (short)
postganglionic neuron (myelinated)
its cell body in peripheral ganglion and projects its axon to an effector; come out cervical/lumbar(long )
autonomic ganglion
collection of sympathetic or parasymathetic postganglionic neuronal cell bodies
dendrites
a short motor neurons branched extension of a nerve cell, along which impulses received from other cells at synapses are transmitted to the cell body. (**responsible primarily for receiving signals from other neurons)
axon hilcock
a specialized part of the cell body (or soma) of a neuron that connects to the axon. The spot where nerves impulses generate here (trigger zone)
nucleolous
organize regions of chromosomes, which contain the genes for pre‐ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA), serve as the foundation for nucleolar structure.
terminal bouton
knoblike distal endings of the terminal branches (usually 10,000or more)
axon
impulse-generating and conducting region
cell body
biosynthetic center and receptive region
tracts
bundles of neuron processes in the CNS
graded potential
short-distance signals
dendritic spines
thorny appendages having bulbous or spiky ends-which represent points of close contact (synapse) with other neurtons
chromatophilic
substance rough with endoplasmic reticulum
nerve fiber
any long axon
motor symbols
o———————–<
prodomindantily skeletal muscle movement
sensory symbols
>——–P————-< (light bulb in middle)
perception of environment; receives various stimuli; may interpret stimuli (i.e. vision); two hemispheres; corpus callosum connects
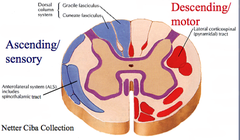
ascending tract
sensory tract; carry signal up the CNS words with “spino”
descending tract
motor tract; carry signal down to PNS word with “spinal”
synapse (have to draw and label)
junction permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another cell (neural or otherwise).
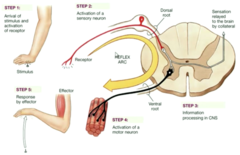
Reflex arc
stimulus, receptor, sensory neuron, intergration center, motor neuron, effector, response
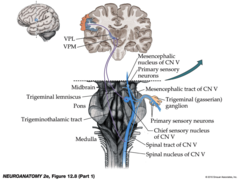
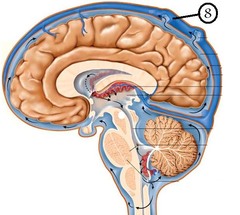
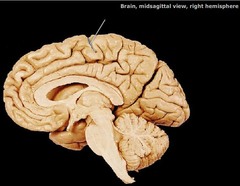
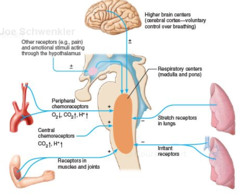
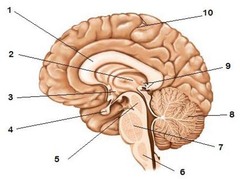
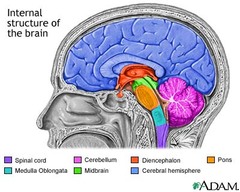
brain stem
The stem-like part of the base of the brain that is connected to the spinal cord. The brain stem controls the involuntary flow of messages between the brain and the rest of the body, and it also controls basic body functions such as breathing, swallowing, heart rate, blood pressure, consciousness, and whether one is awake or sleepy
midbrain
is located between the dicephalon and pons placing it near the center of the brain
pons
contains nuclei that relay signals from the forebrain to the cerebellum, along with nuclei that deal primarily with sleep, respiration, swallowing, bladder control, hearing, equilibrium, taste, eye movement, facial expressions, facial sensation, and posture.
medulla oblongata
helps transfer messages to the spinal cord and the thalamus in the brain from the body and controls breathing, heart function, blood vessel function, digestion, sneezing, and swallowing.
diencephalon
area of brain contains both thalamus and hypothalamus
thalamus
receive sensory input from body organs (sensory cop) and direct these signals to the proper areas/location in the body has 15 nuclei; a relay system
hypothalamus
extensively posterior of the thalamus; controls metabolic i.e. thirst, hunger, blood pressure, temp. etc.
cerebellum
base of brain, function in coordination and muscle activities (balance, reflexes, using multiple muscles/reflexes at once)
cerebrum
sensory association areas in cerebral cortex; responsible for intelligence; thinking, memory (gray mater of brain, interpetation of sensory input)
association
processing of information, interpretation and direction of activities
sensory only (convergent)
I olfactory-smell
II Optic-vision
VII Vestibularcochlear (auditory and balance)
motor only (divergent)
III Oculomotor- eye
IV Trochlear -eye
VI- Abducens- eye
XII- hypoglossal-tongue, swallowing
Mixed (sensory and motor)
V Sensory for face, PTT, motor for adductor jaw muscles
VII Facial -sensory taste, motor facial muscle
IX Glossoparengeal sensory for mouth and motor for larynx (vocalization)
XI Neck (Accessory)
Vagus X- sensory and motor for internal organs; motor for larynx (most extensive cranial nerve)
CNS exits sites
sympathetic thoraric/lumbar
parasymathetic brain (cranial nerves) and sacral
Limbric system in olfactory and gustatory networks
are more of a process than an organ; the main part in the brain and memory system or intergration of sensory and learning. (ie. the pleasant and unpleasant life experiences creates or shapes your personality)
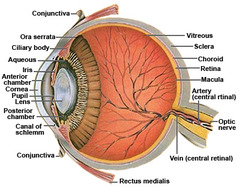
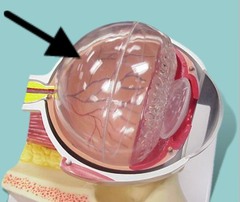
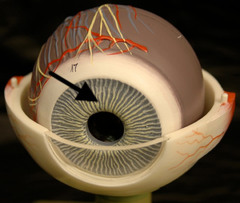
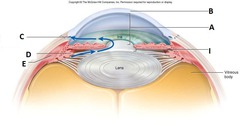
Vitreous humor
back thick part of eye can have filaments that become loose
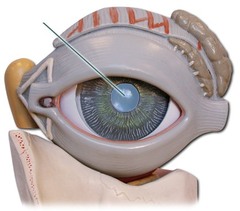
pupil
opening of the iris
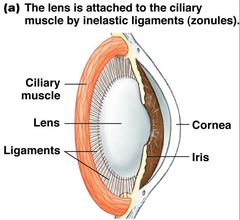
iris
intrinsic smooth muscle, can change size, controlled by the autonomic system (antagonistic)
ciliary muscle
s a ring of smooth muscle in the eye’s middle layer (vascular layer) that controls accommodation for viewing objects at varying distances and regulates the flow of aqueous humour into Schlemm’s canal.
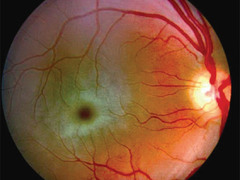
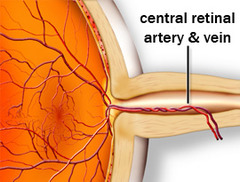
central artery
(retinal artery) branches off the ophthalmic artery, running inferior to the optic nerve within its dural sheath to the eyeball.
scleral venous sinus (Schlemm canal)
the vascular structure encircling the anterior chamber of the eye and through which the aqueous humor is returned to the blood circulation.
optic nerve tract
is an extension of the optic nerve located in the brain.
cornea
is the transparent, dome-shaped window covering the front of the eye. It is a powerful refracting surface, providing 2/3 of the eye’s focusing power.
Process of hearing
Vibrations enter the auricle and travel to the the tympanic membrane. The vibrations continue into the middle ear through the cochlea; travel t0 basilar membrane to the auditory ossicle vessicles vibrate. The pressure is amplifes and waves created by the stapes push into the oval window and move through fluid stimulate auditory cilia activating to association area to the other side of brain to associate sound.
Balance
dynamic equilibrium semicircular canals monitor changes in heads rotation requires our movement for stimulation the fluid in ears as well (cranial nerve VIII)
glands and tear ducts
two tiny openings in the lacrimal puncture tears drain into the lacrimal sac, then into nasolacrimal duct and empties into the nasal cavity at the inferior nasal meatus