Contrast sweetening techniques based on histogram equalisation
Abstract-In computing machine vision applications image sweetening plays an of import function. Recently much work is performed in the field of images enhancement. Many techniques have already been proposed up to now for heightening the digital images. In this paper figure of techniques has been studied, the studyhas shown that how different techniques of contrast sweetening correlative to each other and which technique is efficient to utilize for image sweetening. At the terminal of paper assorted spreads in the literature and its restrictions have discussed.
Keywords—enhancement ; histogram eqaulization ; contrast image.
- Introduction
Digital Image processing is a huge attack used to modify image quality and demo a qualitative consequence in assorted Fieldss like medical images, orbiter images and besides in industrial applications. The attack used to modify the images and to better the quality of the image is called image sweetening. In order to better the quality of the image we deal with brightness and contrast of the image so that information and characteristic should easy extracted from the image while executing the techniques like cleavage, acknowledgment etc. Contrast enhancement tends to better the lucidity of the object in the image by seting the brightness between objects and their backgrounds. Here the procedure of contrast stretching is used that corresponds to supply tonic sweetening which improves and equilibrate the brightness differences between dark, greies and highlight borders of the image. Image enhancement removes the unprompted noise, heighten the borders and besides smoothen the non- unprompted noise. For enhanced image it shows more appropriate consequences than input image and provides more utile in writing show. But enhancement dosage non changes content of image it merely enhances the active scope of selected part so that characteristics can be easy detected. To take different noise different filter is used so ab initio while heightening the image which filter is required to take which type of noise is analyzed and besides to analyse which part of the image needs to heighten in order to pull out the needed information. Image sweetening is performed by utilizing two methods:
- Spatial Domain Methods
- Frequency Domain Methods
In spacial sphere techniques, transmutation operation is straight performed on the image pels and the pel values are updated to heighten the image.
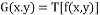
Wheref ( x, Y ) is the input image, G ( x, Y ) is the processed end product image andTrepresents an operation on ‘f’defined over some vicinity of ( x, y ) . Where in Frequency domain foremost the image is transformed to its frequence representation by modifying the spectral transmutation of an image. Second reverse transmutation procedure to the spacial sphere is carried out. It distributes frequence by it high and low scope.The high frequences correspond to pixel values that changerapidly across the image and strong low frequence constituents correspond to big scalefeatures in the image. Assorted techniques of contrast sweetening have been discussed here.
- Histogram equalisation:
Histogram equalisation is a point processing sweetening method that optimizes the contrast of an image by devastation or by equalising the histogram of the image at all points. It improves the local contrast in order to heighten the image. Number of times a value appears in the information set is maintained by histogram tabular array. For an 8-bit image, there will be 256 promising samples in the image and histogram will number the figure of times that each trial value truly occurs in the image. The basic form of a histogram does non convey much valuable information. The form and extension of the histogram straight corresponds to contrast of the image that is narrow histogram distributions are used to stand for low contrast images ; and broad histogram distributions are used to stand for high contrast images as shown in fig 1.
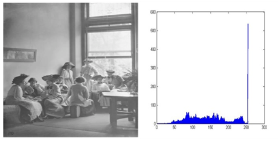
Fig 1a ) input image B ) histogram of input image
- Brightness Continuing Bi-Histogram Equalization ( BBHE )
Bi-histogram equalisation divides the histogram into two parts on the footing of their mean brightness value, represented by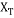 it is the mean strength of all the pels that construct the input image and is called as separation strength. Here histogram that scope 0 to L-1 is divided in two parts as, 0 to
it is the mean strength of all the pels that construct the input image and is called as separation strength. Here histogram that scope 0 to L-1 is divided in two parts as, 0 to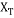 and
and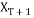 to L-1.
to L-1.
- Dualistic Sub-image Histogram
Equalization ( DSIHE ) :
Harmonizing to this, a histogram is divided into sub-histograms, one which include high strength pels and other with low strength pels. The separation is done on the footing of their average values and each portion equalized with HE technique. At the terminal concluding consequences are obtained, by composing processed sub-images into one image. Histogram equalisation can impact the original brightness of image where BHE and DSIHE conserve the original brightness and get the better of the artefacts generated by Histogram Equalization.
- Adaptive histogram equalisation:
Adaptive histogram equalisation is contrast sweetening technique used in computing machine image processing. The thought behind the technique is that it merely operates on little parts called as tiles of the image, instead than whole image. Every tile ‘s contrast is enhanced, so that the histogram of the end product part should fit the histogram specified by the ‘Distribution ‘ parametric quantity. Bilinear insertion is applied in order to unite the Neighboring tiles which eliminate unnaturally bounds specified above. In contrast, noise elaboration job with homogenous images is non resolved.
- Recursive Mean Separate Histogram Equalization ( RMSHE ) :
RMSHE is used to supply scalable brightness to the image. Here input histogram is divided in two parts on the footing of their several agencies. It is the more usual sweetening and improves the brightness preservation. The images that are failed to heighten by HE and BHE can be enhanced by RMHSE.
II LITERATURE SURVEY
Tyan et Al. for image sweetening Novel algorithms have been proposed utilizing the fuzzed logic with filtering and border sensing. The fuzzed sweetening technique is based on IF… . , THEN… . regulations, which farther modifies the contrast of the image and dynamic scope of grey degree. Fuzzy filtering technique uses Fuzzy rank maps in the frequence sphere and provides better Restoration consequences degraded from linear random noise. The fuzzy border sensing algorithm provides a assortment of information as compared to other method [ 1 ] . Y.S. Choi have proposed a robust fuzzy logic attack based on the conflicting ends of image sweetening like taking impulse noise, smoothing out non-impulse noise, and heightening ( or continuing ) borders and more. For each of the above struggles three different types of filters has been driven with their choice methods based on local context, and predecessor clauses of the fuzzy regulations is obtained. After uniting the consequence of all the filters, the overall consequence of the fuzzed rule-based system is generalized [ 2 ] . F. Farbiz et Al. Have proposed new fuzzy-logic-control based filter that non merely removes unprompted noise, smoothen the Gaussian noise but besides preserve borders at the same clip with one filter. The consequence of this attack has been shown that there is no demand of drifting point computations, a really fast public presentation of the filter as compared to other filter boulder clay than qualitative consequence in border preserving every bit good and supply optimize consequences for complex images [ 3 ] .C. Munteanu et Al. hold introduces an evolutionary optimisation procedure based automatic image sweetening technique. Author describes a fresh nonsubjective criterion for sweetening, and with the several criterion best image get happen but Due its complexness, an evolutionary algorithm ( EA ) as a planetary hunt scheme for best sweetening consequence is given and the algorithm shows superior consequence [ 4 ] .Y.Tokuda et Al. In this survey, the derivation of an image quality accommodation parametric quantity, optimal gamma value is expressed as an optimisation job. Subjectivity, to analyse synergistic evolutionary calculation an image quality enhancement support system is used. After comparing it with a manually derived gamma value, image quality, and derivation clip, this technique has been verified [ 5 ] . Q.Yang represent some nonlinear transform maps author proposed a regularized uncomplete beta map that are most normally used in image contrast sweetening. But the job of adaptively specifying the coefficients of the beta map is still at that place. In image contrast enhancement differential development is applied so that the planetary rapidly search ability of the differential development algorithm, adaptative mutant, the optimum ??›? , ??›? values of beta map can be utilized and an adaptative contrast enhanced image can be formed. To avoid local optimal caparison, a helter-skelter differential development algorithm is proposed [ 6 ] . P. Hoseini has proposed a assorted algorithm, for increasing the contrast a intercrossed algorithm with the combination Genetic Algorithm ( GA ) , Ant Colony Optimization ( ACO ) , and Simulated Annealing ( SA ) . Here in order to obtained contrast sweetening, the planetary transmutation of the input strengths is used and to map the input strengths to the end product strengths ACO algorithm is implemented. It generates local transmutation maps SA which farther modifies the transportation maps of ACO. GA describes the evolutionary procedure of ants’ features [ 7 ] M.I. Quraishi analyze assorted Image Enhancement techniques with different soft calculating techniques such as Bacterial Foraging Optimization, Differential Evolution, Harmony Search, and a intercrossed Particle Swarm Adapted Bacterial and Foraging Optimization algorithm. A new algorithm Particle Swarm Adapted Bacterial Foraging ( PS-BFO ) gives better consequences in the application of relative built-in derivative accountant tuning. Globally the public presentation of the PS-BFO is analyzed on 23 numerical benchmark maps. PS-BFO uses person ‘s best location and the planetary best location in order to seek the waies of tumble behaviour for each bacteria and consequences shows that in most instances PS-BFO performs much better than BFOA. Have done a comparing on three different border sensing attacks based on hunt, fuzzylogic and zero-crossing. Fuzzytechnique is used by one of themforimageenhancement and applied in the country of optical measurings [ 8 ] . P. P. Sarangi et Al. Have discussed a Differential Evolution ( DE ) algorithm and defines its compatibility for seeking optimum solutions which can heighten the contrast in grey graduated table images. Furthermore the solution to work out optimisation jobs an adaptative hunt procedure is given. Here contrast sweetening is performed by grey degree alteration utilizing an nonsubjective parameterized strength transmutation map. Proposed algorithm converts the parametric quantities of the transmutation map by maximising the nonsubjective fittingness standard. For better analyses, consequences of the algorithm has been compared with histogram equalisation, contrast stretching and atom drove optimisation ( PSO ) based image sweetening techniques [ 9 ] . Senthilkumaran et Al. In medical images Magnetic resonance imagination ( MRI ) technique plays a particular function which provides rich information about the human soft tissue anatomy and besides in the procedure of naming assorted encephalon diseases including shot, malignant neoplastic disease, and epilepsy MRI provides knowing information, the basic technique used for MRI in image sweetening is Histogram equalisation. Here the writer shows a brief analyses and comparing on different Techniques like Local histogram equalisation ( LHE ) , Global Histogram Equalization ( GHE ) , Adaptive Histogram Equalization ( AHE ) , Brightness continuing Dynamic Histogram equalisation ( BPDHE ) with different aim and quality step parametric quantities for MRI encephalon image Enhancement [ 10 ] . Mohd. et Al. hold specified that in digital image treating the most simplest and effectual technique is Histogram equalisation ( HE ) but in order to continue the brightness and existent expression of the image the job occurs as during the enhancement procedure the original expression of image is affected. Author proposed several equalisation methods such as Bi- and Multi-histogram equalisation methods which can get the better of the restriction and can continue the original expression of the image. Bi-HE method really enhances the contrast and can continue the brightness every bit good, but the natural expression of the image gets destroyed. So to keep the natural expression of image, Multi-HE methods are proposed, in which the proposed method the histogram of an input image is decomposed into multiple sections and at each section HE is applied independently [ 11 ] . Shamim et Al. proposed an efficient colour image sweetening method for endoscopic images. The enhancement procedure goes through two stairss foremost with the aid of FICE Fuji Intelligent Color Enhancement ) . RGB endoscopic images are converted into three 2-D spectral images and so image with the maximal information is selected as the base image.and in the following phase selected image is used for colour reproduction. In colour reproduction, the chrominance map of an input colour image is added to the base image. This chrominance usher is found by organizing luminosity and composing informations between these two images taking into history vicinity measuring scheme. The separation between luminosity sections of base dark image and beginning shading images is computed using 2-standard Euclidian separation. The proposed technique highlights a per centum of the tissue attributes in the base endoscopic image which will authorise better analysis. The executing of the program is contrasted and other related computations every bit far as reproduction rate, image quality, proficiency of shadowing extension and writhing [ 12 ] . Chang, Yung Tseng, et Al. Shows as traditional histogram methods fails to get the balanced contrast which leads to continue low brightness. Here author gives the mean-variance analysis method to partition the Grey scale image into four bomber images for single image. This technique is proposed to heighten the contrast of the thenar bone X-ray radiogram. Consequence shows that proposed algorithm is better than the planetary histogram equalisation ( GHE ) technique and brightness continuing bi-histogram equalisation ( BBHE ) technique [ 13 ] . Zhigang et Al. have proposed adaptative sweetening algorithm for low light colour image that is for low contrast and brightness. The three measure algorithm foremost performs the planetary brightness adaptative accommodations in which dynamic scope of brightness of image get adaptively adjusted. In the following measure locally adaptative contrast adaptative sweetening is performed by spread outing difference between centre pel and vicinity with brightness average value and discrepancy. And in the last measure colour Restoration is done. Result has shown that dark part item by this algorithm is more efficient and the end product image is more colourful than other techniques [ 14 ] . Raju et Al. have proposed a histogram and fuzzy logic based algorithm which can heighten the low contrast colour images. In this RGB image is converted into HSV and under the control of two parametric quantities M and K, V Component is stretched, where M is considered as mean strength and K is contrast intensification and 128 is taken as value of K [ 15 ] .
III GAPS IN EXISTING WORK
- The bing K factor has been taken statically i.e. 128 by most of research workers.
- Most of the methods depends upon certain predefined regulations no dressed ore on the objects or parts in the given image ; so may imbalance the colour of the end product image.
- Edges plays important function in vision processing but image sweetening technique can degrade the borders excessively.
IV CONCLUSION AND FUTURE WORK:
Many techniques have already been proposed up to now for heightening the digital images. To get the better of the restrictions of earlier techniques a new technique can be proposed which can measure thousand factor automatically utilizing the ant settlement optimisation to happen the best similarity value among the given set of values which represents the image in more efficient mode. The newest attack would hold the ability to hike the contrast in digital images in efficient mode by using the modified border continuing smoothing hypothesis based adaptative k-fuzzy image sweetening algorithm. As border continuing smoothing has ability to cut down the implementation of noise and besides it preserves the borders in efficient mode so provides better consequences.
Mention
[ 1 ] C.Y. Tyan and P.P. Wang, “ Image processing sweetening, filtrating and border sensing utilizing the fuzzy logic attack ” ,2neodymiumIEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems, vol.1, pp.600-605, 1993.
[ 2 ] Y.S. Choi, and R. Krishnapuram, “ A robust attack to image sweetening based on fuzzed logic ” , IEEE Transactions onImage Processing pp.808-825.1997.
[ 3 ] F. Farbiz, S.A Motamedi, and M.B. Mohammad, “ An iterative method for image sweetening based on fuzzed logic ” , IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, vol.5, pp.2937 – 2940,1998.
[ 4 ] C. Munteanu and A. Rosa, “ Gray-scale image sweetening as an automatic procedure driven by development ” , IEEE Transactions on system, Man, and Cyberneticss, Part B: Cyberneticss, vol.34, no.2, pp.1292-1298,2004.
[ 5 ] Y. Tokuda, H. Hashino, G. Ohashi, M. Tsukada, R. Kobayasi and Y. Shimodaira “ Image quality sweetening support system by gamma rectification utilizing synergistic evolutionary calculation ” , IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, pp.2907-2910,2007.
[ 6 ] Q.Yang “ An adaptative image contrast sweetening based on differential development ” , 3rdInternational Congress on. Image and Signal Processing, Vol. 2, pp.631-634, 2010.
[ 7 ] P. Hoseini and M.G. Shayesteh, “ Hybrid Ant Colony Optimization, Genetic Algorithm, and Simulated Annealing for Image Contrast Enhancement ” , IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation, pp.1-6, 2010.
[ 8 ] M.I. Quraishi, J.P. choundar et al. , “ A comparative survey for Image Enhancement utilizing soft calculating theoretical accounts ” World IEEE Congress on. Information and Communication Technologies, pp.697-602, 2012.
[ 9 ] P. P. Sarangi, B.S.P. Mishra, B. Majhi and S. Dehri, “ Gray-level image sweetening utilizing differential development optimisation algorithm ” , International Conference on Signal Processing and Integrated Networks, Pp.95-100, 2014.
[ 10 ] N. Senthilkumaran and J. Thimmiaraja, “ Histogram equalisation for image sweetening utilizing MRI encephalon images ” , World Congress on Computing and Communication Technologies, pp. 80-83, 2014.
[ 11 ] M.F. Khan, E. Khan, Z.A. Abbasi, “ Multi section histogram equalisation for brightness continuing contrast sweetening ” , Springer Advances in Computer Science, Engineering & A ; Applications, pp. 193-202, 2012.
[ 12 ] Imtiaz, M. Shamim and K. Wahid, “ A colour reproduction method with image sweetening for endoscopic images ” , Middle East Conference on Biomedical Engineering, 2014.
[ 13 ] Chang, T. Yung, et Al. “ Contrast Enhancement in Palm Bone Image Using Quad-Histogram Equalization” , IEEE International Symposium on Computer, Consumer and Control, pp. 1091-1094, 2014.
[ 14 ] Z. Zhou, N. Sang, X. Hu, “ Global brightness and local contrast adaptative sweetening for low light colour image” , Optik-International Journal for Light and Electron Optics, no. 6, pp.1795-1799, 2014.
[ 15 ] G. Raju, and M.S. Nair, “A fast and efficient colour image sweetening method based on fuzzy-logic and histogram” , International Elsevier Journal of Electronics and Communications, vol.68, no.3, pp.237–243, 2014.





