Introduction:
Microscope is an equipment which is used to detect unseeable atoms and it is chiefly used in the research labs for medical and forensic scrutinies ( Wheeler and Wilson, 2011 ) . In the 16Thursdaycentury, Janssen and his boy pes forwarded the 1stmodern microscope by infixing several lenses into a cylinder ( Chen, Zheng and Liu, 2011 ) . The 1stcompound microscope designed by Janssen contained merely two bulging lenses and proved that, the basic construct of a compound microscope is that an object can be enlarged consecutive by two convex lenses ( Chen, Zheng and Liu, 2011 ) . Anthony new wave Leeuwenhoek ( 1632-1723 ) was the first individual who invented a microscope which was powerful plenty to detect the unseeable micro beings ( Kent, 2000 ) . A compound visible radiation microscope fundamentally contains two chief lenses called optic lens and the nonsubjective lens ( Kent, 2000 ) . The deciding power of a compound light microscope is about 0.2 micro metres, it seems that the deciding power of a compound light microscope is about 1,000 times better than the deciding power of a normal human oculus ( Engelkirk and Duben-Engelkirk, 2008 ) . The concluding magnification power ( M ) of a compound light microscope is the generation of the powers of the optic lens and the nonsubjective lens ( MConcluding= Mobjtens Moc”) ( Murphy and Davidson, 2012 ) .
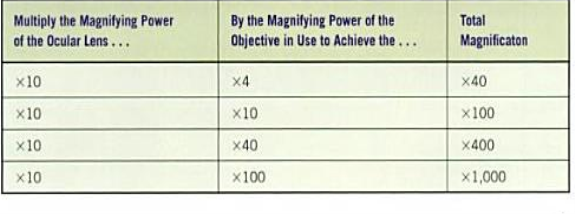
Table 1: Entire magnification of a compound visible radiation microscope ( Engelkirk and Duben-Engelkirk, 2008, p.129 ) .
While working in a compound visible radiation microscope, the user must be more concerned about the lenses present in it, as the nonsubjective lens consist of a aggregation of convex lenses in order to give more magnification and a slide quiver could damage the lenses ( Amitrano and Tortora, 2012 ) . Components of a compound visible radiation microscope are optic lens/ ocular, go arounding nosepiece, nonsubjective lenses, phase, phase accommodation boss, capacitor, condenser control boss, iris stop control arm, field stop lever, rheostat control boss, harsh accommodation boss and all right accommodation boss ( Engelkirk and Duben-Engelkirk, 2008 ) .
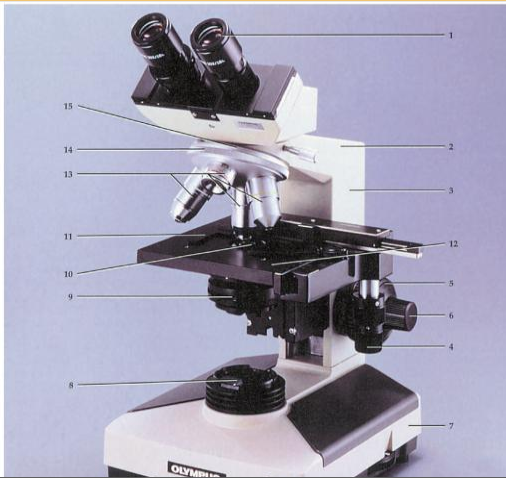
Figure 1: Labeled diagram of a compound visible radiation microscope ( Amitrano and Tortora, 2012 ) .
- Eyepiece
- Body tubing
- Arm
- Mechanical phase boss
- Coarse accommodation
- Fine accommodation
- Base
- Sub phase lamp
- Diaphragm
- Capacitor
- Phase cartridge holder
- Phase
- Aims
- Nose piece
- Revolving nose piece
|
Components |
Location |
Functions |
|
Ocular lens/ ocular |
Is the upper most of the microscope |
X 10 magnification |
|
Revolving nosepiece |
Above the phase |
Holds the nonsubjective lenses |
|
Objective lenses |
Held in topographic point above the phase by the go arounding nosepiece |
Used to amplify objects placed on the phase |
|
Phase |
Directly beneath the nosepiece and nonsubjective lenses |
Flat surface on which the specimen is placed |
|
Phase accommodation boss |
Beneath the phase |
Used to travel the phase and specimen |
|
Capacitor |
Directly beneath the phase |
Contains a lens system that focuses visible radiation on the specimen |
|
Condenser control boss |
Beneath and to one side of the capacitor |
Used to set the tallness of the capacitor |
|
Iris stop control arm |
Attached to the capacitor |
Used to set the sum of visible radiation emitted from the capacitor |
|
Field stop lever |
Beneath the capacitor and aggregator lens |
Used to set the sum of visible radiation coming through the aggregator lens |
|
Rheostat control boss |
At the forepart of the base |
Used to set the sum of light being emitted by the light bulb in the base |
|
Coarse accommodation |
On the arm of the microscope, near the base |
Used to concentrate the lenses |
|
Fine accommodation |
On the arm of the microscope, near the base |
Used to concentrate the lenses |
Table 2: Components of a compound visible radiation microscope, locations and their maps( Engelkirk and Duben-Engelkirk, 2008, p.129 ) .
The innovation of the compound light microscope promoted a important development in the Fieldss of biological science and medical specialty ( Chen, Zheng and Liu, 2011 ) . “By geting the microscopic and diseased images of the infective micro-organism, medical research workers have established a series of new academic topics, including bacteriology, immunology, virology, cell pathology, and others. In peculiar, the innovation of negatron microscopes has raised the observation of the traditional pathology from the cellular degree to the sub-cellular level” ( Chen, Zheng and Liu, 2011, p.07 ) .
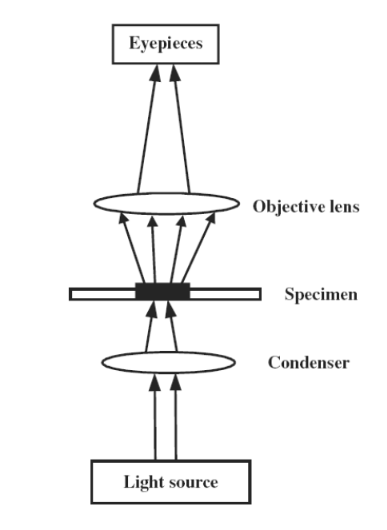
Figure 2: Illustration of optical tract of a Compound visible radiation microscope ( Chen, Zheng and Liu, 2011, p.18 ) .
Aims:
- To place the parts of a compound light microscope and their maps.
- To detect pre-prepared histological slides.
Materials:
- Compound light microscope
- Pre-prepared histological slides
Methodology:
The compound light microscope was switched on and ensured the strength of the visible radiation was in the minimal degree. The flag was ensured whether it is to the full opened. Then the pre-prepared histological slide ( Artery sec. ) was placed on the phase by hold oning the slide by the outer edges with the pollex and forward finger. The scanning power ( 4X ) aim lens was selected with more attention and heard the “click” sound when the lens was decently fixed on its place. Then the phase was raised up utilizing the harsh accommodation by detecting from the side until the slide is about touching the nonsubjective lens. The capacitor was brought to its lowest place. Then the phase was lowered down utilizing the harsh accommodation boss while looking through the optic lens. When the specimen was clearly focused, the discoloration and the gross anatomy was clearly observed. Then the image of the clearly focussed specimen was observed by the supervisor.
Then the phase was somewhat lowered and the high power ( 40X ) aim lens was selected. Again the phase was raised up until the aim lens about touches the slide, while looking from the side. The strength of the visible radiation was increased to its upper limit and the capacitor was raised up to its upper limit in order to acquire more light beams through the lens. Then the phase was lowered down easy utilizing the all right accommodation boss while looking through the optic lens. . When the specimen was clearly focused, the discoloration and the gross anatomy was clearly observed. Then the image of the clearly focussed specimen was observed by the supervisor. The slide was removed from the phase carefully and the microscope was brought to its old place to see the 2neodymiumpre-prepared histological slide.
The 2neodymiumpre-prepared histological slide was an ovary specimen. The 2neodymiumspecimen besides observed under the scanning power and the high power by the same process which was done for the 1stspecimen. Then the image of the clearly focussed specimen was observed by the supervisor. After finishing the observations, the images of the specimen were drown in the log book.
After finishing the whole practical, the phase, light strength and the capacitor were brought to their original places.
 Consequences:
Consequences:
Artery sec 40X

Artery sec 400X

Ovary sec 40X

Ovary sec 400X
Discussion:
Decision:
Mentions
Amitrano, R. and Tortora, G. ( 2012 ) ( a )Update: Lab exercisings in anatomy and physiology with cat dissections. Google Books[ Online ] . Available at: hypertext transfer protocol: //books.google.lk/books? id=yTsLAAAAQBAJ & A ; pg=PA1 & A ; dq=compound+light+microscope & A ; hl=en & A ; sa=X & A ; ei=lvcXVf75L43huQTU5YDIDg & A ; redir_esc=y # v=onepage & A ; q=compound % 20light % 20microscope & A ; f=false ( Accessed: 30 March 2015 ) .
Amitrano, R. and Tortora, G. ( 2012 ) ( B )Update: Lab exercisings in anatomy and physiology with cat dissections.Belmont: Brooks/ Cole, p.02, figure.
Chen, X. , Zheng, B. and Liu, H. ( 2011 ) ( a ) ‘optical and digital microscopic imaging techniques and applications in pathology’ , National Institute of Health Public Access, 34 ( 1-2 ) , pp. 1-22 [ Online ] DOI: 10.3233/ACP-2011-0006 ( Accessed: 01 March 2015 ) .
Engelkirk, P.G. and Duben-Engelkirk, J.L. ( 2008 ) ( a )Laboratory diagnosing of infective diseases: Necessities of diagnostic microbiology. Google Books[ Online ] . Available at: hypertext transfer protocol: //books.google.lk/books? id=l56-WMdyqzcC & A ; pg=PA130 & A ; dq=compound+light+microscope & A ; hl=en & A ; sa=X & A ; ei=lvcXVf75L43huQTU5YDIDg & A ; redir_esc=y # v=onepage & A ; q=compound % 20light % 20microscope & A ; f=false ( Accessed: 31 March 2015 ) .
Engelkirk, P.G. and Duben-Engelkirk, J.L. ( 2008 ) ( B )Laboratory diagnosing of infective diseases: Necessities of diagnostic microbiology.Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, p.129, tabular array.
Kent, M. ( 2000 )Advanced biological science. Google Books[ Online ] . Available at: hypertext transfer protocol: //books.google.lk/books? id=8aw4ZWLABQkC & A ; dq=compound+light+microscope & A ; source=gbs_navlinks_s ( Accessed: 30 March 2015 ) .
Murphy, D.B. and Davidson, M.W. ( 2012 ) ( degree Celsius )Fundamentalss of light microscopy and electronic imagination. Google Books[ Online ] . Available at: hypertext transfer protocol: //books.google.lk/books? id=f8qhtqRjxQMC & A ; dq=compound+light+microscope & A ; source=gbs_navlinks_s ( Accessed: 31 March 2015 ) .
Wheeler, B and Wilson, L.J. ( 2011 ) ( B )Practical forensic microscopy: A research lab manual. Google Books[ Online ] . Available at: hypertext transfer protocol: //books.google.lk/books? id=qhha1srnESYC & A ; dq=compound+light+microscope & A ; source=gbs_navlinks_s ( Accessed: 31 March 2015 ) .
1





