Abstract
Malaysia is a federal constitutional monarchy located in Southeast Asia. It consists of 13 provinces and three federal districts and has a entire land mass of 329,847 square kilometres separated by the South China Sea into two likewise sized parts, Peninsular Malaysia and East Malaysia.
The purpose of this study was to speaking about the system and the disposal construction of Malaysia. First, we will present the history of the state. Second, we will elaborate the system and disposal construction of Malaysia. Then we will discourse Malaysia’s function and part at the universe degree. And eventually, discourse the differences and resemblances in system and the disposal construction between China and Malaysia to understand these two states good.
Introduction
Malaysia is a state in South East Asia whose strategic sea-lane place brought trade and foreign influences that basically influenced its history. Hindu and Buddhist civilizations imported from India dominated early Malayan history. They reached their extremum in the Sumatran-based Srivijaya civilization, whose influence extended through Sumatra, Java, the Malay Peninsula and much of Borneo from the 7th to the fourteenth centuries.
Although Muslims had passed through Malaysia every bit early as the tenth century, it was non until the 14th and 15th centuries that Islam foremost established itself on the Malay Peninsula. The acceptance of Islam by the fifteenth century saw the rise of figure sultanates, the most outstanding of which was the Melaka ( Malacca ) . Muslim civilization has had a profound influence on the Malay people, but has besides been influenced by them.
The Portuguese were the first European colonial powers to set up themselves in Malaysia, capturing Malacca in 1511, followed by the Dutch. However, it was the British, who after ab initio set uping bases at Jesselton, Kuching, Penang, and Singapore, finally secured their hegemony across the district that is now Malaysia. The Anglo-Dutch Treaty of 1824 defined the boundaries between British Malaya and the Netherlands East Indies ( which became Indonesia ) .
A 4th stage of foreign influence was in-migration of Chinese and Indian workers to run into the demands of the colonial economic system created by the British in the Malay Peninsula and Borneo. Nipponese invasion during World War II ended British domination in Malaysia. The subsequent business of Malaya, North Borneo and Sarawak from 1942 to 1945 unleashed patriotism.
In the Peninsula, the Malayan Communist Party took up weaponries against the British. A tough military response was needed to stop the insurgence and convey about the constitution of an independent, multi-racial Federation of Malaya in 1957. On 31 August 1963, the British districts in North Borneo and Singapore were granted independency and formed Malaysia with the Peninsular provinces on 16 September 1963. Approximately two old ages subsequently, the Malayan parliament passed a measure to divide Singapore from the Federation. A confrontation with Indonesia occurred in the early-1960s.
Race public violences in 1969 led to the infliction of exigency regulation, and a curtailment of political life and civil autonomies which has ne’er been to the full reversed. Since 1970 the “ National Front alliance ” headed by United Malays National Organization ( UMNO ) has governed Malaysia. Economic growing dramatically increased life criterions by the 1990s. This turning prosperity helped minimise political discontent.
Literature reappraisal
The development of socio-cultural facets
Malaysia is a constitutional monarchy state Constitutional monarchy ( constitutional monarchy divided into monarchy and parliamentary monarchy, parliamentary monarchy belongs to Malaysia ) . Due to historical grounds, Sarawak and Sabah provinces have greater liberty. Malaysia ‘s caput of province called the Supreme Head of State, while the largest party in the House of Commons by the authorities or alliance composed of leaders is the Prime Minister. Its political system is inherited from the British Westminster system.
Malaya was the largest manufacturer of Sn, gum elastic and palm oil in the universe at one clip. Fabrication has a big influence in the state ‘s economic system. Malaysia is the universe ‘s largest Islamic banking and fiscal centre. In 2012, the economic system of Malaysia was the 3rd largest economic system in South East Asia behind more thickly settled Indonesia and Thailand and 29th largest economic system in the universe by buying power para with gross domestic merchandise bases at US $ 492.4 billion and per capita US $ 16,922. As one of three states that control the Strait of Malacca, international trade plays a big function in its economic system.
Malayan society public assistance keeps increasing these old ages. With its extremely developed sense of household and kin duty, the authorities has by and large encouraged voluntary societal public assistance activities and has subsidized plans of private groups. The authorities ‘s plan of public aid takes the signifier of hard currency, trade goods, and institutional attention. Children ‘s services provide case-work services and administer kids ‘s places. A probation service provides attention and aid for juvenile delinquents and dependants, and a disabled individuals ‘ service AIDSs the deaf, deaf-and-dumb person, and blind. In add-on, attention is provided for the aged and inveterate ill.
A provident fund has provided lump-sum benefits for old age, disablement, and decease. Pensions are funded by 11 % parts of net incomes by workers, and 12 % of paysheet by employers. The retirement age is 55. Work hurt insurance and disablement pensions to low-income workers is available, with a particular system for public employees.
Administrative machinery of the state
BRANCHES OF GOVERNMENT
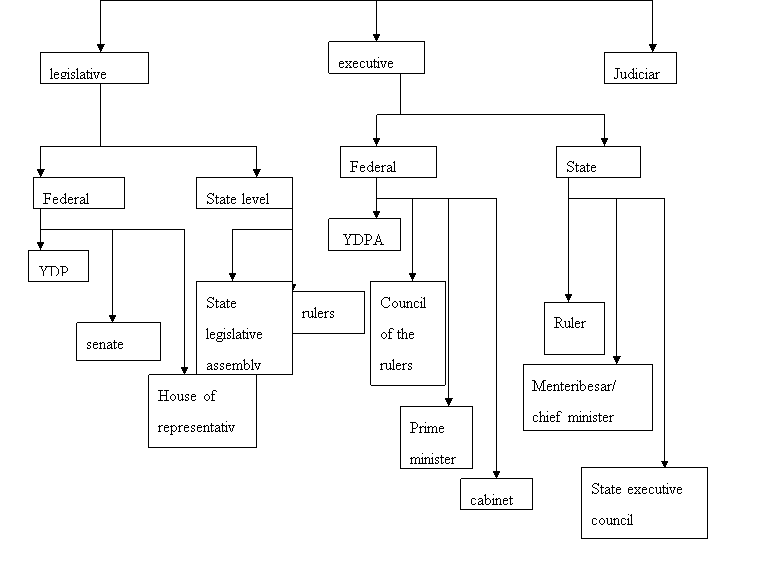


Legislative
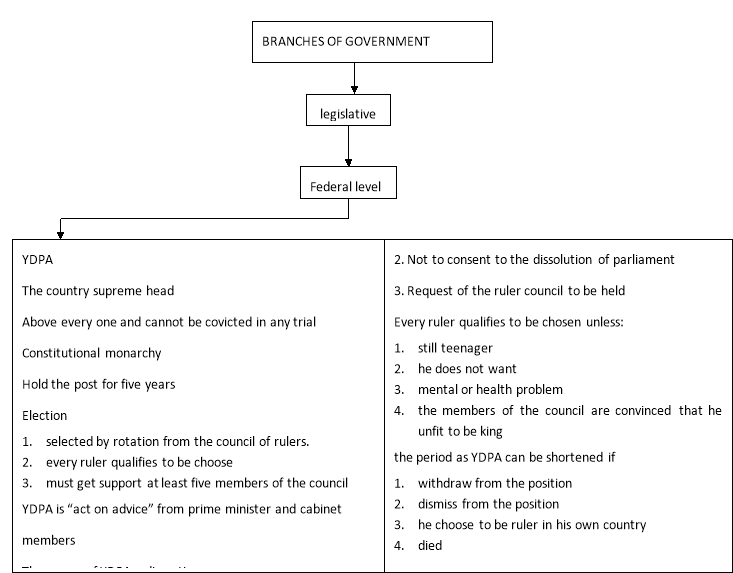
Legislative power is divided between federal and province legislative assemblies. The bicameral parliament consists of the lower house, the House of Representatives or dewan Negara ( literally the “Chamber of the Nation” ) . All 70 Senate members sit for three-year footings ( to a upper limit of two footings ) ; 26 are elected by the 13 province assemblies and forty-four are appointed by the male monarch based on the advice of the Prime Minister. Parliament has a maximal authorization of five old ages by jurisprudence.
The male monarch may fade out parliament at any clip, and normally does so upon the advice of the Prime Minister. General elections must be held within sivty yearss of the disintegration of parliament. I pattern, this has meant that elections have been held every three to five old ages at the discretion of the Prime Minister.
Legislative power divided between federal and province legislative assemblies. Malaysia has two beginnings of jurisprudence. The national fundamental law, the nation’s supreme jurisprudence, can be amended by a tow-thirds bulk in parliament. ( Since its formation, the VN has ne’er lacked the necessary two0thirds until 2008”s General Election )
The 2nd beginning of jurisprudence is syariah ( Muslim jurisprudence ) , which applies merely to Muslims. Ther federal authorities has small input into the disposal of syariah ; it falls to the provinces to implement Islamic jurisprudence, and readings vary from province to province. The parliament follows a multi-party system and the regulating organic structure is elected through a first-past-the station system.
Executive
Executive power is vested in the cabinet led by the Prime Minister, the Malayan fundamental law stipulates that the premier curate must be a member of the Lower House of parliament who, in the sentiment of the Yang di-Pertuan Agong ( YDPA ) , commands a bulk in parliament. The cabinet is chosen from among members of both houses of Parliament and is responsible to that organic structure.
The executive subdivision of the authorities consists of the Prime Minister as the caput of the authorities, followed by the assorted curates of the Cabinet. Strictly talking, the Executive subdivision does non hold the right to step in in the Legislative or Judicial subdivisions of the province. This is to guarantee that the rule of separation of power is adhered to, as guaranteed by Article 127 of the Federal Constitution.
Judicial
The bench is theoretically independent of the executive and the legislative assembly, although protagonists of the authorities hold many judicial places. The highest tribunal in the judicial system is the Federal Court, followed by he Court of Appeal, and two High Courts, one for Peninsular Malaysia, and one for East Malaysia. The subsidiary tribunals in each of these legal powers include Sessions Courts, Magistrates’Courts, and tribunals for Children. Malaysia besides has a Particular Court to hear instances brought by or against all Royalty.
There is besides a Particular Court, established in 1993 to hear instances brought by or against Ruler. Before its constitution, Rulers were immune from any proceedings brought against them in their personal capacity. Rulers include the Yang di-Petuan Agong, and the caputs of province of Malaysia’s constituent provinces.
Separate from the civil tribunals are the Syariah Courts, which decide on instances which involve Malayan Muslims. These tribunals run parallel to the normal tribunal system, and are undergoing reforms that include the first of all time assignment of female Judgess. Argument exists in Malaysian over whether the state should be secular of Islamic. Some province authoritiess controlled by the Pan-Malaysian Islamic Party, including that of Terengganu, have passed Islamic Torahs, but these have non gone into consequence due to resistance from the federal authorities.
31 August 1957 at Selangor nine, the brotherhood Jack ( British flag ) was brought down and jalur gemilang was flown. The official sign language of the declaration of independency took topographic point in Merdeka Stadium. Federation’s first cabinet of curate was announced together with the assignment of Tunku Abdul Rahman as the first premier curate. Tuanku Adbul Rahman ( Negeri Sembilan ) was chosen the first Yang Dipertuan Agong of the federation of Malaya.
Method and stuffs
This study was conducted by informations aggregation. Datas came from professional literature and official web sites. We checked out the informations carefully to do certain we could acquire right consequences. No undependable information was used. Analysis was based on nonsubjective world without any personal positions.


Malaysia’s part
Over the old ages, Malaysia has developed a scope of advanced fiscal instruments to run into both its particular needs every bit good as in the context of altering planetary environment. These instruments have enhanced and enriched the economic armory of developing states in conveying about structural alterations in their economic systems, without being unduly dependant on the text book theoretical accounts of western economic experts. Here are a few of the major fiscal instruments that Malaysia has developed.
New Economic Policy
The aim of the New Economic Policy ( NEP ) was to cut down poorness of race and to heighten the economic wellbeing of the Bumiputras in the context of an spread outing. This construct of development where growing is linked to distribution in an optimum manner could be really utile to states with a multi-racial population, made up of autochthonal and immigrant population.
Bilateral Payments Assignment
Malaysia developed the bilateral payments agreement as an instrument to advance its trade with developing states. Other developing states can utilize this instrument to cut down their dependance on the western developed states.
Selective exchange control government
The selective exchange control steps, stands out as the most important new and advanced fiscal instrument in the scope of instruments that Malaysia has developed over the old ages. It could turn out to be a really utile instrument for many states, peculiarly developing states, who want to guarantee stableness in their fiscal systems so that they can concentrate on growing.
Chinese system and disposal construction
China ‘s political system is the system of people ‘s Congress. The people ‘s Congress system is China ‘s people of all cultural groups in China under the leading of the Communist Party, harmonizing to the rule of democratic centralism, elected by the National People ‘s Congress and local people ‘s Congresss at all degrees, and to the people ‘s Congress as the footing, the constitution of all province establishments, recognizing the people be in power system. The people ‘s Congress system is China ‘s people ‘s political power building experience and alone creative activity, is a merchandise of Marx ‘s province theory and combined with the status of our state.
The people ‘s Congress system is our state ‘s government, is China ‘s cardinal political system, but besides the basic signifier of our state be in power for the people. Adhering to and honing China ‘s people ‘s Congress system, we should continue from the national conditions of our state, sum up the practical experience of my ain, and at the same clip, learn from the accomplishments of political civilisation of world, but ne’er copy the Western theoretical account of political system. To beef up building of system, the realisation of the socialist democracy institutionalization, standardisation and process.
Findingss
China and Malaysia officially established diplomatic dealingss on May 31, 1970.As lifting stars of developing states all over the universe. China and Malaysia have many common issues during development. Malaysia was one of the four Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelams in 1990s when it has a high growing rate. And now, China developing in a high rate to be far in front in the universe at the present. How to maintain native society stable and GDP growing rate increasing are our common issues. Both China and Malaysia should larn from each other’s development history for a nice hereafter.
Reference list
- Jayum A. jawan ( 2002 )political relations and authorities in Malaysia.Shah alam: karisma publications.
- Nazaruddin hj. Mohd gaol et.al ( 2001 )pengajian Malaysia,learner hall: Selangor
- Nazaruddin hajji mohd gaol, ma’rof redzuan, asnarulkhadi abu samah dan ismail hj mohd Rashid. ( 2004 ) .Pengajian Malaya: kengaraan dan kewarganegaraan.Edisi kedua.Petaling jaya. Prentice hall.
- hypertext transfer protocol: //en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Federation_of_Malaya
- hypertext transfer protocol: //my.china-embassy.org/chn/malaysia/mlxygk/t174743.htm





