Introduction
The cost of a undertaking should be scheduled prior to the execution of building, due to the scarceness of investing undertakings, the client needs to cognize to construct it in line with the cost of his design, and other characteristics, structural and aesthetic demands.
The intent of this study is to name the stairss which are necessary to enable the Chartered Quantity Surveyors to carry on a comprehensive pre-contract cost planning and control, from brief to develop the proposed undertaking client through different design stage until the stamp was eventually accepted.
Pre-contract cost planning, cost control is where to travel, in other words the cost of pre-contract plan entirely can non prolong without pre-contract cost control, and frailty versa procedure. Success in the building procedure of cost control and planning of the cardinal warrant for the undertaking. The most complex undertakings, have a common subject, they are fraught with hazards and uncertainnesss that could take to increased costs, cost control is the control of the cost of the strategy cost public presentation, adjust the undertaking in one or another mention to altering process fiscal environment. It is advised to go on to guarantee that the concluding cost of this procedure within the mark scope of costs in building undertakings throughout the building period. Cost control can be divided into three chief countries, which are in the design stage, and building began at the stamp phase controlled by the client after completion.
Pre-contract cost planning and cost controlling
Cost Planning
Pre-contract costs are to be allocated by the planning budget to the building of the undertaking is expected to supply proficient design squad to bring forth a successful design balance cost model within which the assorted elements. Cost Planning occurred stamp phase, and after traveling to the cost value of work, it is designed and executed before. Cost programs are normally many determinations are made before the edifice design. It provides a comprehensive image of the whole economic system.
Cost Controling
Pre-contract cost control is a procedure, which enables the set down budget for the undertaking to command within the bound. During the design due class and determination taken, the cost program needed to be revised to do certain that the determinations will non be unwanted for the planned amount.
By an effectual building cost control system, director can compare the updated cost with the criterion program, by supervising the updated cost, and at that place by appropriate actions can be adhered to retain the cost with in recognized scope.
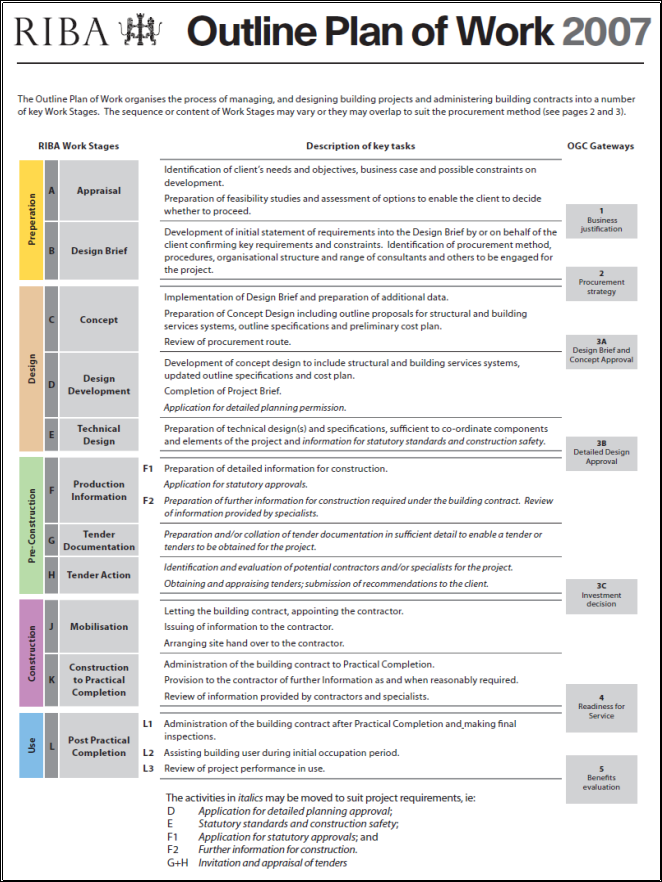
Pre-contract cost planning and cost commanding procedure with regard to the RlBA program of work
|
RIBA Plan of Work Stages |
Procedure ( Purpose of work & A ; undertakings to be done ) |
Peoples Directly Involved |
|
Pre-stage A |
Establishing the Need |
|
|
Client Team, Undertaking Manager, designers |
|
|
Work Phase A |
Options Appraisal |
|
|
Client Team, Undertaking director, designers, applied scientists and QS harmonizing to nature of specializer undertaking |
|
|
Work Phase B |
Strategic Briefing |
|
Reappraisal with Client alternate attacks and cost and clip deductions
|
Client Team, Project director, designers, applied scientists and QS harmonizing to nature of specializer undertaking |
|
|
Work Stage C |
Outline proposals |
|
|
All client involvements, designers, applied scientists, QS and specializers as required. |
|
|
Work Stage D |
Scheme design |
|
|
Architects, applied scientists and specializers, all statutory and other Approving governments. |
|
|
Work Stage E |
Detailed design |
|
|
||
|
Work Stage F |
Production information |
|
|
Architects, applied scientists and specializers, contractor ( if appointed ) , |
( Beginning: Infusion and modified from RIBA Standard Form of Agreement for the Appointment of an Architect 1 and the Architect’s Job Book 2. )
Life Cycle Costing
Explanation in term of Life Cycle Costing
Life rhythm cost means “The sum discounted value of the cost of ownership, operation, care and disposal of edifices or edifice systems” over a period of clip.
It has long been recognized that to measure the cost of edifices on the footing of their initial costs entirely is unsatisfactory. Some consideration must besides be given to the costs-in-use that will be necessary during the life clip of edifice. This latter factor will be influenced by the type of Client and will be a more of import consideration to some than others.
Different grades of importance will hence be attributed to cost-in-use factors depending on whether the undertaking is to be constructed for sale, rental or proprietor business.
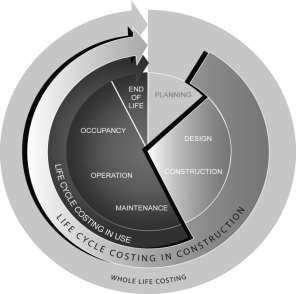
Building related costs can be classs as follows:
- Initial costs ( Purchase, Acquisition, Construction costs, Land costs, Legal costs, professional fee etc ) .
- Energy and Water cost ( Energy use, Energy monetary values, H2O cost ) .
- Operation, Maintenance, and Repair costs.
- Replacement cost.
- Residual Values ( Release/Salvage values/disposal costs ) .
- Finance charges
- Social costs ( Non-monetary benefits or cost ) .
Advantages of Life Cycle Costing
- Life rhythm costing will assist directors to understand acquisition costs versus runing and support costs.
- Enables you to compare different combinations of steps and take the 1 that will maximise your nest eggs and fiscal return.
- Reduces your investing hazard by projecting a more complete image of the hereafter. And it will assist for better pricing with the more realistic costs.
- Life rhythm bing will give earlier consequences in actions to bring forth gross or to cut down the costs, and chances for costs decrease.
- It is better determinations can be made as we can hold a better overview of grosss and costs for the whole life of the merchandise.
Disadvantages of Life Cycle Costing
- Life rhythm costing is non an exact scientific discipline. A life rhythm cost analysis does non supply an exact figure of the costs ; it simply gives an penetration in the major cost factors and an penetration into the magnitude of the costs.
- The life rhythm cost estimation is merely an estimation. Estimates can ne’er be more accurate than the inputs and the inputs are frequently estimates themselves or adept sentiments.
- Life rhythm cost theoretical accounts require volumes of informations and merely a few smattering of informations likely to be when carry oning the estimation. Therefore many premises have to be made.
- Life rhythm cost consequences are used for several intents and, in some cases, are non compatible.
Explanation of feasibleness assessment of the edifice
Options assessments are undertaken following the completion of feasibleness surveies. Their intent is to measure a figure of possible options before developing a construct design for the preferable option.
Feasibility surveies do non affect ‘ design ‘ as such. They are preliminary surveies whose intent is to:
- Establish whether the undertaking is feasible.
- Aid in the development of the strategic brief.
- Aid in the designation of executable options.
After measuring the feasibleness surveies, the client will make up one’s mind which options the adviser squad should develop. Does non hold more than four options, ideally over at this phase. If there are more options exist, there may be need for farther high-level survey prior to a more elaborate analysis options to measure. Optionsare non designs, they are diagrammatic options surveies that enable the clientto understand the wide pros and cons of the available options so that a preferable option can be selected.
These surveies allow farther appraisals and treatments:
- The CDM co-coordinator ( if appointed at this phase ) can measure the hazards of the options in relation to the CDM ordinances.
- The designer can organize audiences with the local authorization and other statutory governments, and assesses possible be aftering permission demands and other statutory demands ( such as the demand for an environmental impact appraisal for the options ) .
- The cost adviser can fix initial cost assessments of the options.
Fixing assessments for these options may necessitate farther site studies or site information. It may besides be necessary to committee extra advice, such as planning advice, expertness on rights of visible radiation, technology advice, or other specializer services depending on the complexness of the undertaking. The demand to committee other advisers will frequently be determined by the graduated table and location of a development and besides by the client ’s acquaintance with the site and the local country. Large-scale development of belowground restraints will about surely require expertness in the early phases of the undertaking, but may non remain in the traditional street. However, both may necessitate local governments or other legal apprehension of consular maps.
The lead adviser can so organize the readying of a bill of exchange options review study, from which the client can either choose a preferable option or teach the development of farther options or assessments.
The options review study might incorporate:
- A general description of the options.
- Diagrammatic study layouts.
- The overall effects of each option for the client’s operations.
- Appraisal of compatibility with the clients vision, mission and aims.
- Appraisal of the overall feasibleness of each option.
- Potential for future-proofing.
- Planing permission issues ( including the possible demand for an environmental impact appraisal ) .
- Sustainability considerations.
- Impact on the local community and environment.
- Third-party dependences.
- Value direction exercisings.
- Whole-life costs with a fundamental appraisal of costs /sqm, constellation and service.
- Time-frames, phasing and cardinal mileposts.
- Procurement path.
- Hazards.
- Recommendations.
At this phase the client ’s brief is likely to spread out, partially from the decisions of feasibleness assessments but besides from cognition gained by research into be aftering case in points, legal issues, technology informations and the proficient restraints and nature of the undertaking.
Once a preferable option has been selected, the adviser squad may transport out farther appraisals to help the client in fixing a concern instance and undertaking executing program for the preferable option before construct design begins.
Cost patterning techniques in cost planning
Definitions
Ferry et Al. ( 1997 )
“ The symbolic representation a system, showing the content of that system in footings of the factors which influence its costs ”
Seeley ( 1996 )
“ A process developed to reflect, by agencies of derived procedures, adequately acceptable end product for an constituted series of input informations ”
Ashworth ( 1999 )
“ Techniques used for calculating the estimated cost of a proposed building undertaking “costs” . “data” . “project” .
Type of Construction Cost Modeling
Cost appraisal theoretical accounts can be classified into three chief
coevalss:
Traditional theoretical account
- Conference,
- Fiscal method
- Functional unit
- Superficial
- Superficial margin
- Cube
- Storey enclosure
- Approximate measure
- Bill of measures
Non-traditional theoretical account
- Statistical / Econometric theoretical account ( Regression analysis and Causal theoretical account ) ,
- Hazard / Simulation theoretical account ( Monte Carlo simulation and Value
- direction )
- Knowledge -based theoretical account
- Resource based theoretical account
- Life rhythm theoretical account
Value direction
Value Management
Value Management in Construction Undertakings
Value Management is a structured facilitated procedure in which determination shapers, stakeholders, proficient specializers and others work collaboratively to convey about value based outcomes in systems, procedures, merchandises and undertakings.
Value Management throughout the undertaking rhythm – usually, a undertaking has a organized sequence of categories integrated with the undertaking plan beginning at project description- ideal degree, and repeating through to building proficient degree. During the functional degree, lessons discovered categories and station tenancy appraisal surveies bettering future undertakings in add-on to the employment of the new service.
Cost cut downing Versus Value Improvement is for the past old ages, value analysis and value technology were associated with cost decrease. But through implementing value methods on undertakings, it became clear that best value was non about cost decrease, but instead assisting the apprehension of the client’s demands and concern demands. This is now of import to the present construct of Value Management in Construction industry.
Aim of Value Management
The aims of Value Management as a procedure tool to better efficiency and cost effectivity in geting and pull offing fixed assets, besides in plans, systems and procedures.
Reasons for unneeded cost that lead to hapless value
- Lack of Information ;
- Lack of Idea ;
- Incorrect Beliefs, Habits and Attitudes ;
- Impermanent fortunes ;
- Honest incorrect beliefs ;
- Changes in proprietor demands ;
- Outdated criterions and specifications.
When should a value technology survey be undertaken
The application of value technology as a formal technique will mostly depend on the value of a peculiar undertaking and the degree of hazard involved.
|
High value |
Low Value |
|
|
High hazard |
Strategic critical |
Strategic security |
|
Low hazard |
Tactical net income |
Tactical acquisition |
For ‘strategic-critical’ undertakings ( high hazard, high value ) a full value technology process is about ever justified. For ‘strategic-security’ ( high hazard, low value ) and ‘tactical-profit’ ( low hazard, high value ) undertakings, desktop value technology surveies will frequently do, provided there is input from all stakeholders. For ‘tactical-acquisition’ ( low hazard, low value ) undertakings a value technology exercising is non normally necessary.
Techniques used in value direction
Techniques used in value direction as a combination of constructs and methods to make sustainable value for both organisation and their stakeholders. Some of techniques are specific to Value Management are below.
- Cost Benefit Analysis – Cost benefit analysis is an accounting tool used to compare the costs of establishing a merchandise line. The basic regulation of pollex is that resources should be spent merely if making so will achieve company ends in relation to the costs of those resources.
- Criteria Weighing Technique – The standards weighing technique is used to hit aims through leaden enumeration.
- Five Ws and the H – Ask “ Who? ” “ What? ” “ Where? ” “ When? ” “ Why? ” and “ How? ” This technique brings the cardinal issues to visible radiation and examine them to place the job or chance.
- Function Analysis System Technique ( FAST ) – The FAST technique identifies the major maps involved in making merchandises or services and looks at how each map creates value for the company and its clients. The FAST would so find whether holding the machines cleaned every other hebdomad would be more cost effectual without aching the quality of production.
- Procedure Mapping – Through the usage of flow charts, procedure function analyzes each procedure step-by-step to find whether a measure is losing or merely wasting clip. Procedure function is normally used in fabrication.
- Hazard Analysis – Hazard analysis is a fiscal tool used to place hazards that can potentially impact the merchandise, service, undertaking or procedure. The analysis looks at the costs involved, clip restraints and other variables that may negatively impact the result.
- SWOT Analysis – SWOT is an acronym that stands for “ strengths, failings, chances and menaces, ” which is exactly what the SWOT analysis aims to place.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Value Management
Advantages of Value Management
- Reduce undertaking costs
- Improve design efficiency
- Optimize value for money
- Concentrate design attempt
- Advance design determinations
- Improve ways to follow with the brief
- Afford and independent functional reappraisal
Disadvantages of Value Management
- Extra work for bing undertaking squad, which is non ever reimbursed, as it is at the client’s discretion
- Break to project squad
- Can incur excess fees
- Can widen design period





