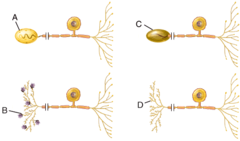
H) axon terminals
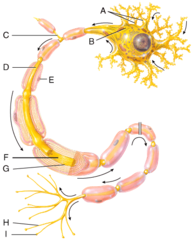
In the diagram, where are axon terminals?
dendrites
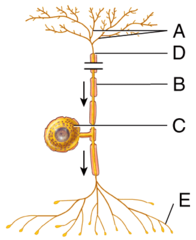
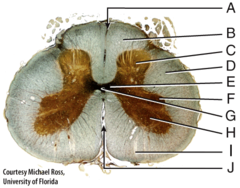
Which of the following structures is labeled A in the diagram?
cell body
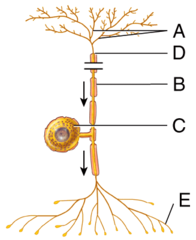
Which of the following structures is labeled C in the diagram?
E) myelin sheath
This structure electrically insulates the axon of a neuron to increase the speed of nerve impulse conduction.
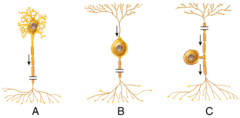
Type I cutaneous mechanoreceptor (Merkel disc)
What specific type of unipolar neuron is shown in the diagram labeled B?
multipolar neuron
What is the structural classification of the neuron labeled A?
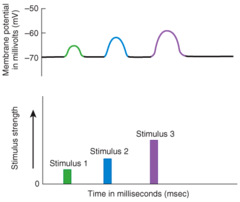
Spatial summation
When summation results from buildup of neurotransmitter released simultaneously by several presynaptic end bulbs, it is called
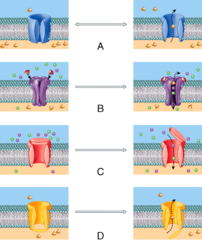
A) leak channel
Which of these types of channels is involved in leaking sodium and potassium ions across the membrane in order to establish the resting potential of a cell?
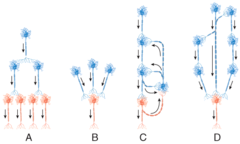
C) reverberating circuit
Which diagram represents a reverberating circuit?
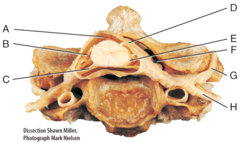
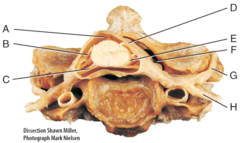
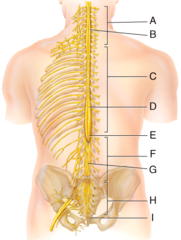
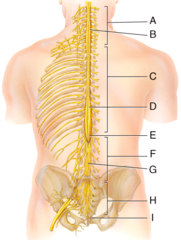
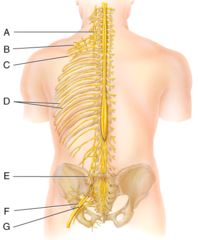
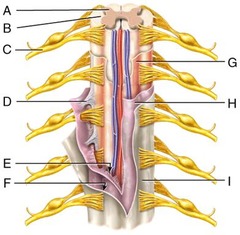
C) anterior(ventral) root of spinal cord
Which of the labeled structures carries exclusively motor information away from the spinal cord?
G) posterior ramus
Where is the posterior ramus?
I) anterior white column
Where is the anterior white column?
D) Lumbar enlargement
Which of the following structures is labeled D in the diagram?
I) coccygeal nerves
The structure labeled I in the diagram belongs to which group of spinal nerves?
E) femoral nerve
Which of the following nerves is labeled E in the diagram?
F) subdural space
Where is the subdural space?
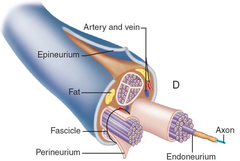
perineurium
The indicated region is the
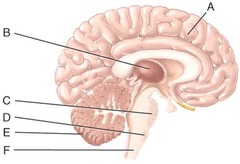
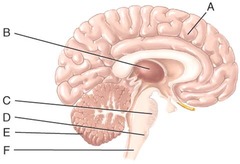
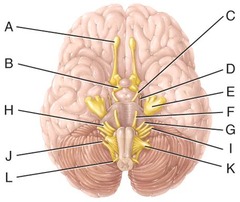
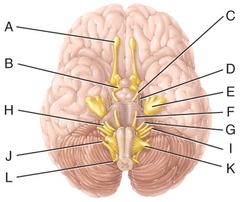
B) thalamus
Which of the labeled structures in the diagram is the thalamus?
E) cerebellum
This major portion of the brain is used to monitor movements initiated by the motor areas of the cerebrum.
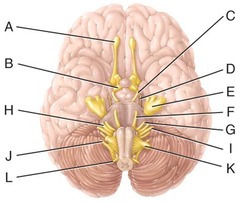
B) optic nerve
Which cranial nerve in the diagram is primarily involved in the sense of vision?
C) oculomotor nerve
Which cranial nerve in the diagram has an autonomic motor function primarily involved in near vision accommodation and constriction of the pupil?
E) trigeminal nerve
Which cranial nerve in the diagram has a somatic motor function primarily involved in chewing?
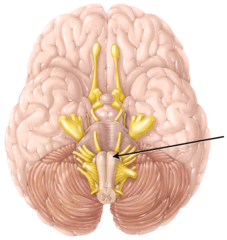
pyramids; it contains nuclei for equilibrium and movements of the eyeball
Which statement is NOT true about the indicated region?
Acetylcholine
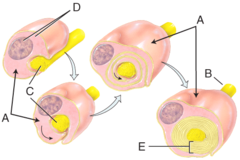
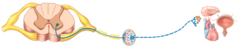
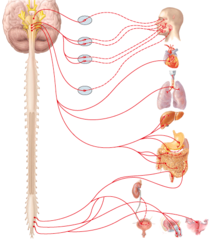
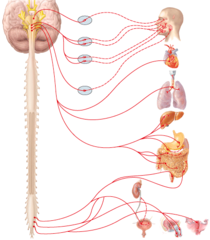
If the pathway shown in the diagram is a parasympathetic division pathway, which neurotransmitter acts at the effector?
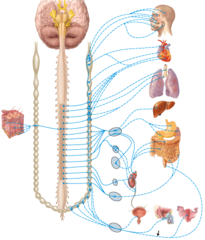
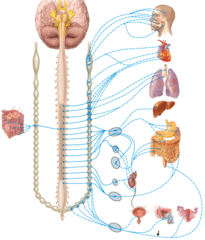
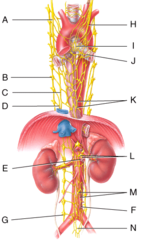
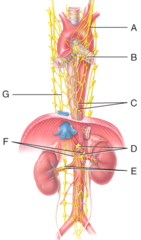
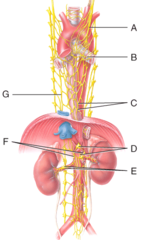
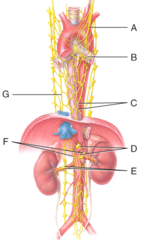
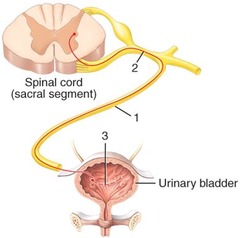
Autonomic motor pathway
What type of nervous system pathway is shown in the figure?
sympathetic postganglionic neurons.
The indicated structures contain
Celiac ganglion
Which ganglion supplies the stomach with postganglionic neurons?
parotid gland.
Postganglionic neurons from the otic ganglion supply the
X vagus nerve
Parasympathetic innervation of the liver occurs through
M) mesenteric ganglion and plexus
Where is the inferior mesenteric ganglion and plexus in the figure?
A) left vagus
Where is the left vagus (X) nerve in the diagram?
C) esophageal plexus
Where is the esophageal plexus in the diagram?
E) renal plexus
Where is the renal ganglion and renal plexus in the diagram?
parasympathetic postganglionic neuron.
The structure labeled 3 in the diagram is a
D) Acetylcholine
What type of neurotransmitter is used by the pathway shown in the figure?
Remember! This essay was written by a student
You can get a custom paper by one of our expert writers
Order custom paper
Without paying upfront