Analysis of Imidacloprid in Nutrient Trade Goods
Introduction
Imidacloprid is a systemic chloro-nicotinyl insect powder which blocks the microtinergic neural tract, hence it is used for bar of insects and plagues like rice hoppers, aphids, ticks, white fly and white ants. It is normally used on veggies and fruits like murphy, cotton, sugar Beta vulgariss and soya bean. It is besides used on workss like rice and corn. In the Indian market, Imidacloprid is available in the trade products- Gaucho and Confidor which are used for seed intervention and for foliage and dirt intervention severally ( Kapoor et al. , 2013 ) . Its usage as a permutation for other insect powders is increasing. It is chiefly used on rice, cereals, maize murphy, veggies sugar Beta vulgaris, fruit and cotton ( Arora, 2009 ) . It is besides used in seed intervention and dressing of dirt ( Jemecet al. ,2007 ) . Residual information of environmental destiny of imidacloprid are conflicting, while some writers considered it as comparatively still in dirt and do non expect its flight to land H2O ( Tomlin, 1997 & A ; Krohn and Hellpointner, 2002 ) .However some surveies indicate the contrary statements ( Armbrust and Peeler, 2002 )
Increased usage of pesticides have resulted in pollution of the environment and besides caused effects on human wellness changing from short-run effects to long term effects. Short term effects include mild symptoms such as concerns and sickness while long term effects may include happening of diseases like malignant neoplastic disease, generative injury, and endocrinal break ( Chenet al. ,2011 ) .Due to the possible hazard of pesticides for human wellness, its usage in agribusiness should be subjected to regular monitoring ( Kapoor et al. , 2013 ) . The periodical analysis of pesticide residues in nutrient trade goods is indispensable for its judicial usage in the involvement of public wellness. Unfortunately, negligible informations are available on the sum of imidacloprid in nutrient trade goods sold in local markets of Lucknow part in India ( Kapoor et al. , 2013 ) .
In position of big graduated table usage of imidacloprid and scarceness of Indian literature ( Gajbhiye, et al. , 2004 ) it is indispensable to measure present environmental burden of imidacloprid residues in different nutrient trade goods as imidacloprid is supposed to be toxic chemical ( Tomizawa and Casida, 2003 & A ; 2005 ; Kapooret al. , 2010 & A ; 2011 ;Bhardwajet al. , 2010 )It is hence imperative to analyse imidacloprid residues in veggies, fruits, cereals, fruit juices and babe nutrients samples in and around, Lucknow metropolis, India, during 2010-2011.The survey besides determines the estimated day-to-day consumption of imidacloprid exposure of local population of Lucknow metropolis, India by devouring the above analyzed nutrient trade goods.
Methodology
Samples were collected during October 2010 to July 2011 from chief markets of Lucknow metropolis, India. Total of 250 samples of five different nutrient trade goods ( veggies, fruits, cereals, fruit juices and pamper nutrient ) consisting 10 samples of each were collected. Analyzed fruits were apple, banana, orange, grapes and Punica granatums. Vegetables selected for survey were chou, Brassica oleracea botrytis, tomato, murphy, okra, eggplant, and pepper ; and cereals were wheat, rice and pulsations. Fruit juices were Mangifera indicas, Psidium littorale, Ananas comosus, orange and lichee and babe nutrients coded as BF-1 to BF-5 were taken. Ingredients of babe nutrient ( BF1-5 ) are as follows: BF-1: wheat and Milk, BF-2: apple, wheat and milk ; BF-3: banana, wheat and milk ; BF -4: honey, wheat and milk ; BF -5: rice, wheat and milk. Polythene bags were used for aggregation of samples. Samples after aggregation were transported to research lab and were analyzed at the earliest or stored at 4a-¦C until analysis. Samples were subjected to HPLC and LC-MS analysis after proper clean-up and extraction of samples. Recovery surveies and quality control was besides done.
Consequences
Validation of method for finding of imidacloprid in different nutrient trade goods
In this method recovery variableness in different concentration of Imidacloprid ( 0.0625, 0.125, 0.25 and 0.5mg Kg-1) in different trade goods ranges from 77.55 to 111 % and RSD ranged from 5.22 % to 14.16 % . The LOD for imidacloprid in the present survey was in scope from 0.004 to 0.01 milligrams Kg-1. The LOQ for imidacloprid in the present survey ranged from 0.014 to 0.070 milligrams Kg-1. Calibration standard curves for HPLC was R2=0.992. Standard chromatogram of imidacloprid by HPLC and its LC-MS analysis are shown in Fig 4.1 & A ; 4.2
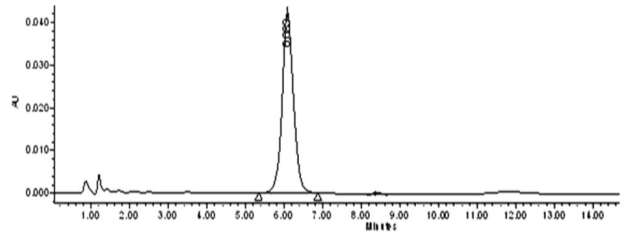
Fig 4.1: HPLC Chromatogram of criterion of imidacloprid.
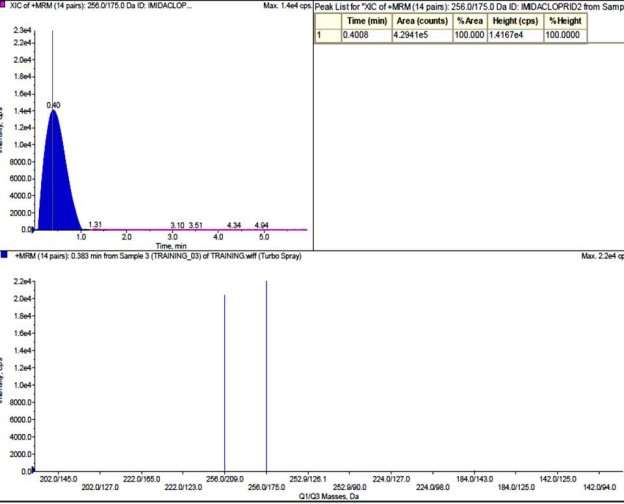
Fig 4.2:Detection of imidacloprid by mass spectroscopy. MS/MS spectra of the m/z 256 parent ion, exhibiting the merchandise ions of imidacloprid at m/z 209 and at m/z 175.
Analysis of Imidacloprid in different nutrient trade goods
Imidacloprid was detected in 44 samples out of 256 samples. In these, 8 samples were more than MRL ( maximal residue bound ) preset by Prevention of Food Adulteration Act. ( PFA ) , Govt. of India 1954, CODEX. , 2006. ( Table 4.1 & A ; Fig. 4.3 )
Table 4.1:Maximal Residual Limit ( MRL ) of imidacloprid in different nutrient trade goods
| Commodity | *MRL ( mg kilogram-1) PFA/Codex |
| Grapes | 0.5 |
| Cabbage | 0.5 |
| Cauliflower | 0.5 |
| Potato | 0.5 |
| Wheat | 0.05 |
| Rice | 0.05 |
Entire 250 samples were analyzed for presence of imidacloprid in which 38 samples were found to be contaminated with imidacloprid, nevertheless merely 6 samples showed concentration of imidacloprid above than their corresponding MRL ( Fig 4.3 and table 4.2 ) . The degree of imidacloprid residues in assorted trade goods were compared with their MRL. Presences of imidacloprid in fruits like apple were ( 0.02-0.26 milligram kg-1 ) , Banana ( 0.04 milligram kilogram-1) , Orange ( 0.01-0.13 ) and Grapes ( 0.04 – 0.78 milligram kilogram-1) . Imidacloprid in veggies like chou was ( 0.08-0.89 ) mg kg-1, Cauliflower ( 0.45mg kilogram-1) , Potato ( 0.19-1.32 ) , Tomato ( 0.24-0.46 ) and Okra ( 0.11 milligram kilogram-1) and Capsicum ( 0.45 ) . Presences of imidacloprid in Cereals like Wheat I was 0.01-0.10 mg kg-1 ) , Wheat II ( 0.02 – 0.10 milligram kilogram-1) , Rice I ( 0.01-0.05 ) , Rice II ( 0.004-0.03 ) and Pulses ( 0.006 – 0.05 milligram kilogram-1) ( Table3.3 ) . None of samples of fruit juices showed presence of imidacloprid. Besides none of different babe nutrients were found to be contaminated with presence of imidacloprid. Maximal taint was in cereals & gt ; veggies & gt ; fruits ( Figure 4.4 ) .
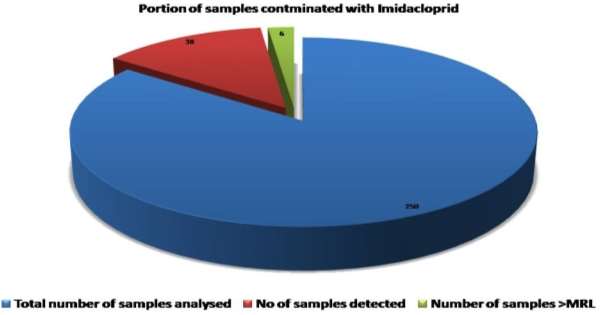
Fig. 4.3Number of samples detected with imidacloprid residues and figure of samples detected with Imidacloprid greater than MRL values in all nutrient trade goods
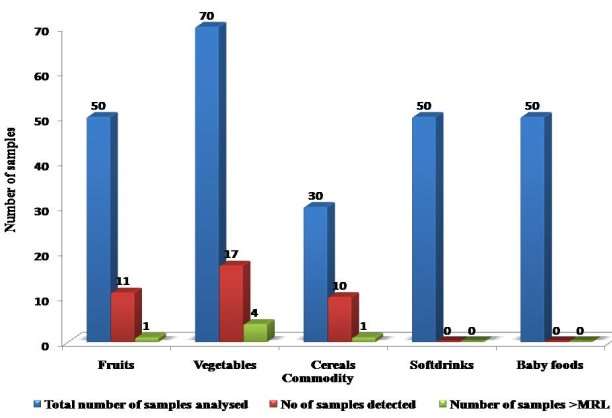
Fig. 4.4Presence of imidacloprid residues in different nutrient trade goods
Table 4.2:Average Levels, concentration scope and frequences of imidacloprid residues in different nutrient trade goods.
| Commodity | Samples | Mean
( mg /kg ) |
Residues range ( mg /kg ) | No of samples | No of samples above MRL ( mg /kg ) | |
| Analyzed | Detected | |||||
| Fruits | Apple | 0.04±0.02 | 0.02-0.26 | 10 | 3 | 0 |
| Banana | 0.005±0.004 | ND-0.04 | 10 | 1 | 0 | |
| Orange | 0.02±0.01 | 0.019-0.13 | 10 | 4 | 0 | |
| Grapes | 0.13±0.08 | 0.04-0.78 | 10 | 3 | 1 ( 0.5 ) | |
| Pomegranate | Neodymium | Neodymium | 10 | 0 | 0 | |
| Vegetables | Cabbage | 0.15±0.11 | 0.08-0.89 | 10 | 3 | 1 ( 0.5 ) |
| Cauliflower | 0.21±0.12 | 0.29-0.93 | 10 | 3 | 1 ( 0.5 ) | |
| Tomato | 0.08±0.06 | 0.24-0.46 | 10 | 2 | 0 | |
| Potato | 0.32±0.17 | 0.19-1.32 | 10 | 4 | 2 ( 0.5 ) | |
| Okra | 0.01±0.01 | ND-0.11 | 10 | 1 | 0 | |
| Eggplant | 0.06±0.03 | 0.13-0.21 | 10 | 3 | 0 | |
| Capsicum | 0.05±0.05 | ND-0.45 | 10 | 1 | 0 | |
| Cereals | Wheat | 0.01±0.01 | 0.01-0.10 | 10 | 3 | 1 ( 0.05 ) |
| Rice | 0.009±0.005 | 0.01-0.05 | 10 | 4 | 0 | |
| Pulsations | 0.008±0.005 | 0.016-0.05 | 10 | 3 | 0 | |
| Fruit juices | Mango | Neodymium | Neodymium | 10 | 0 | 0 |
| Guava | Neodymium | Neodymium | 10 | 0 | 0 | |
| Pineapple | Neodymium | Neodymium | 10 | 0 | 0 | |
| Orange | Neodymium | Neodymium | 10 | 0 | 0 | |
| Litchi | Neodymium | Neodymium | 10 | 0 | 0 | |
| Baby Foods | BF-1 | Neodymium | Neodymium | 10 | 0 | 0 |
| BF-2 | Neodymium | Neodymium | 10 | 0 | 0 | |
| BF-3 | Neodymium | Neodymium | 10 | 0 | 0 | |
| BF-4 | Neodymium | Neodymium | 10 | 0 | 0 | |
| BF-5 | Neodymium | Neodymium | 10 | 0 | 0 | |
| Gross Total | 250 | 38 | 6 | |||
Valuess represent mean± Se of 10 samples.Valuess in parenthesis indicate several MRL ( CODEX, 2005 )
The EDIs have been calculated between 0.004 to 0.131 µg/kg organic structure weight/day, while the jeopardy indices ( EDI/ADI ) ranged from 0.007 to 0.218 for the tried trade goods ( Table 4.3 )
Table 4.3:Calculation of estimated day-to-day consumption ( µg/kg b.w/day ) and hazard index appraisal of imidacloprid in assorted nutrient trade goods
| Commodity | Average concentration of imidacloprid in trade good ( ?C ) ( µg/kg ) | Average one-year consumption of trade good per individual ( kilogram )( F ) | No. of yearss in twelvemonth ( D ) | Average weight of individual ( W ) | ADI ( µg/kg b.w/day ) | EDI ( µg/kg b.w/day ) | Hazard index ( % ) |
| Fruits # | 39 | 9.5 | 365 | 60 | 60 | 0.016 | 0.028 |
| Vegetables # | 125 | 23 | 365 | 60 | 60 | 0.131 | 0.218 |
| Wheat* | 10 | 52.8 | 365 | 60 | 60 | 0.024 | 0.040 |
| Rice* | 9 | 66 | 365 | 60 | 60 | 0.027 | 0.045 |
| Pulses* | 8 | 12 | 365 | 60 | 60 | 0.004 | 0.007 |
# NNMB study 2005-2006, *NSSO, 1975-2000
Discussion
Entire 250 samples were analyzed. 50 samples each of fruits, fruit juices and babe nutrients, 70 samples of veggies and 30 samples of cereals were analyzed for presence of imidacloprid residues. None of the samples of fruit juices and babe nutrients showed presence of imidacloprid. Similar consequences have been reported in surveies of Turkey and Brazil which have showed absence of pesticides residues in fruit juices ( Topuzet al. , 2005, Furlani et al. , 2011 ) .However, the hints of pesticides in fruit based soft drinks of Spain have been besides reported ( Garcia-Reyeset Al. , 2008 ) . Therefore, these two nutrient trade goods may be free from imidacloprid because of their processing. However imidacloprid was detected in 38 samples consisting fruits, veggies and cereals which is around 15.20 % of entire samples. In 22 % samples of fruits, presence of imidacloprid was observed out of which 2 % of samples were above to their several MRL.
Degree of imidacloprid in apple ranged from 0.02-0.26 mg/ kilogram, banana from ND-0.04 mg/ kilogram, orange from 0.019-0.13 mg/ kilogram and grapes from 0.04 – 0.78 mg/ kilogram ( Table 4.2 ) . Imidacloprid was non detected in any of the samples of Punica granatum. However one sample of grape has shown the residue of imidacloprid above to MRL ( 0.50 mg/ kilogram ) . Although in 24 % of vegetable samples imidacloprid was detected but merely 5.71 % have shown presence of imidacloprid above their several MRL ( Kapoor et al. , 2013 ) .
The presence of imidacloprid residues was in following order murphy & gt ; cauliflower & gt ; chou & gt ; tomato & gt ; brinjal & gt ; pepper & gt ; okra. 33 % samples of cereals have shown presence of imidacloprid but merely 3 % of samples were above their several MRL fixed by PFA ( 0.05 mg /kg ) . Imidacloprid residues have been besides reported in veggies and fruits samples of Palestine. In the survey it was found that the imidacloprid concentration in some harvests of Palestine was more than their MRLs ( Daraghmeh et al. , 2007 ) . In several surveies of Almeria, Spain, it was found that out of 200 samples of fruits and veggies analyzed,25-53 % ( mean 21 % ) of samples showed presence of imidacloprid residues ( Fernandez-Alba et al. , 2000 )
Many states have legal directive to command degree of pesticide residues in nutrient through upper limit residue bound ( MRL ) for protection of consumer’s wellness [ ( PFA ( 1954 ) & A ; ( WHO, 2003 ) . The degree of pesticides residues in nutrient trade goods are legislative to minimise exposure of consumer’s to unneeded consumption of pesticide and to guarantee their careful usage. From point of view of human wellness, it is indispensable to compare exposure estimations to find toxicological standards such as estimate day-to-day consumption ( EDI )
Consequences of this survey have been used to cipher EDI. The unit of EDI is microgram pesticides per kg organic structure weight per twenty-four hours ( µg/kg b.w/day ) . The EDI is a existent appraisal of pesticide exposure calculated as per the international guidelines ( WHO, 1997 and Osmanet al. , 2011 )utilizing following equation: EDI=?C x F/D x W
where C is the norm of imidacloprid concentration in each trade good ( µg/kg ) ; F is average one-year consumption of nutrient per individual ( Kg ) ; D is figure of yearss in a twelvemonth i.e. 365 and W signifies the mean organic structure weight of human organic structure i.e.60 kilogram ( Kapoor et al. , 2013 )
The one-year consumption per individual as sum of fruits, veggies, wheat, rice, pulses is 9.5, 23, 52.8, 66, 12 kg/year severally harmonizing to Indian study performed in the old ages 1975-2000 ; 2005-2006 ( NNMB,1979-2008 and NSSO,1975-2000 ) . Average of imidacloprid in each nutrient trade good, one-year ingestion of single trade goods per individual, the estimated day-to-day consumption ( EDI ) and acceptable day-to-day consumptions ( ADI ) ( µg/kg organic structure weight/day ) are compared in Table 4.3. ADI are besides established by international organisations like FAO & A ; WHO ( FAO, 2002 & A ; 2004 ) . The EDIs have been calculated between 0.004 to 0.131 µg/kg organic structure weight/day, while the jeopardy indices ( EDI/ADI ) ranged from 0.007 to 0.218 for the tested nutrient samples.
Hence it is shown that lifetime ingestion of trade goods like veggies, fruits, fruit juices, babe nutrients, wheat, rice and pulsations may non do wellness jeopardies for the population of Lucknow metropolis, India ( Darko and Akoto. , 2008 ) since the jeopardy indices for imidacloprid residues were less than one. It has been reported in a survey that common place processing removes important sum of pesticides residues from veggies ( Nath and srivastava, 1990 ) ( Kapoor et al. , 2013 )
Hence hazard of wellness jeopardy because of imidacloprid residue in trade goods like veggies, fruits, fruit juices, babe nutrients, wheat, rice and pulsations does non make dismaying state of affairs and therefore may non be of great concern. Monitoring of pesticides residues in nutrient is priority aim of pesticide research to avoid possible hazard to human wellness. Monitoring of pesticide residues is a cardinal tool for guaranting conformity of good agribusiness patterns. Therefore, periodical monitoring of pesticides residues in nutrient is really of import to supply counsel on the judicial usage of pesticide in the involvement of public wellness
Decision
The present survey showed mild happening of imidacloprid residues in analyzed nutrient trade goods collected from Lucknow metropolis, India. It is hence indicated that life clip ingestion of veggies, fruits, fruit juices, babe nutrients, wheat, rice and pulsations may non exhibit wellness jeopardy for population of Lucknow metropolis, India since the jeopardy indices for imidacloprid residues were less than one. Therefore the hazard of wellness jeopardies due to imidacloprid residues in these nutrient trade goods may non be of great concern for population of Lucknow metropolis, India.
Therefore, imidacloprid residues in these nutrient trade goods may non present any wellness jeopardies to the population of Lucknow metropolis, India. The findings of the survey besides suggest that periodical monitoring of imidacloprid residues should be carried out in other nutrient trade goods every bit good at national degree to forestall and minimise wellness hazards. Although our consequences indicate negligible hazard associated with exposure of imidacloprid, particular safeguards should be taken to cut down entire exposure to this chemical from assorted nutrients. A periodical monitoring of imidacloprid in other nutrients trade goods like non-vegetarian diet are the recent demand for consumers every bit good as governments of nutrient quality control ( Kapoor et al. , 2013 ) .





